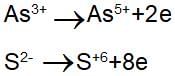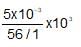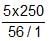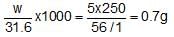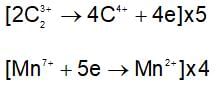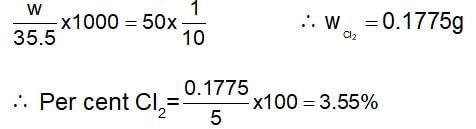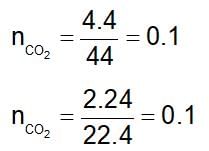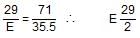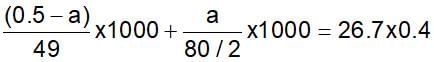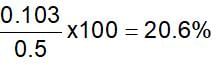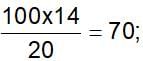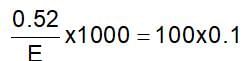Mole & Redox Reaction - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Mole & Redox Reaction
What is the mass of Fe304 if it reacts completely with 25 ml of 0.3m K2Cr2O7?
One mole of a mixture of CO and CO2 requires exactly 20 g of NaOH in solution for complete conversion of all the CO2 into Na2CO3 .How much NaOH would it require for conversion into Na2CO3, if the mixture (one mole) is completely oxidised to CO2?
1.60 g of a metal were dissolved in HNO3 to prepare its nitate. The nitrate on strong heating gives 2 g of its oxide. The equivalent weight of metal is:
The maximum amount of BaSO4 precipitated on mixing 20 mL of 0.5 M BaCI2 with 20 mL of 1 M H2SO4
What is the [OH-) in the final solution prepared by mixing 20.0 mL of 0.050 M HCI with 30.0 mL of 0.10 M Ba(OH)2?
The brown ring complex [Fe(H2O)5NO+]SO4 has oxidation number of Fe:
0.5 mole of H2SO4 is mixed with 0.2 mole of Ca(OH)2 The maximum number of mole of CaSO4 formed is:
Volume of 0.1 M NaOH needed for the neutralisation of 20 mL of 0.05 M oxalic acid is:
How many garm of KMnO4 should be taken to make up 250 mL of a solution of such strength that 1 mL is equivalent to 5.0 mg of Fe in FeSO4?
25 mL of 0.50 M H2O2 solution is added to 50 mL of 0.20 M KMnO4 in acidic solution. Which of the following statements is true?
What volume of 0.40 M Na2S2O3 would be required to react with the I2 liberated by adding excess of KI to 50 mL of 0.20 M CuSO4 solution?
The number of mole of potassium salt, i.e, KHC2O4.H2C2O4.2H2O oxidised by one mole of permanganate ion is:
5 g of a sample of bleaching powder is treated with excess acetic acid and KI solution. The liberated I2 required 50 mL of N/10 hypo. The percentage of available chlorine in the sample is:
4.4 g of CO2 and 2.24 litre of H2 at STP are mixed in a container. The total number of molecules present in the container will be:
20 g of an acid furnishes 0.5 moles of H3O+ ions in its aqueous solution. The value of 1 g eq. of the acid will be.
The chloride of a metal contains 71 % chlorine by weight and the vapour density of it is 50. The atomic weight of the metal will be:
The simplest formula of a compound containing 50% of element X (at. wt. 10) and 50% of element Y (at. wt. 20) is:
One g of a mixture of Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 consumes y equivalent of HCI for complete neutralisation. One g of the mixture is strongly heated, then cooled and the residue treated with HCI how many equivalent of HCI would be required for com-plete neutralisation?
0.5 g of fuming H2SO4 (oleum) is diluted with water. This solution is completely neutralised by 26.7 mL of 0.4 N NaOH. The percentage of free SO3 in the sample is:
Equivalent weight of bivalent metal is 32.7. Molecular weight of its chloride is:
If 20% nitrogen is present in a compound, it’s minimum molecular weight will be.
0.52 g of a dibasic acid required 100 mL of 0.1 N NaOH for complete neutralisation. The equivalent weight of acid is:


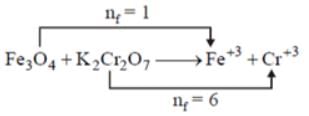 neqFe3O4 = neq K2Cr2O7
neqFe3O4 = neq K2Cr2O7
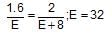


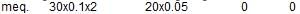
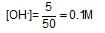
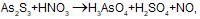 the element oxidised is/are
the element oxidised is/are