Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Electrostatic Potential - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Electrostatic Potential
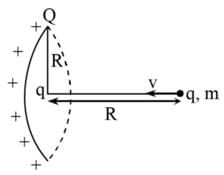
The minimum velocity v with which charge q should be projected so that it manages to reach the centre of the ring starting from the position shown in figure is

According to the standard convention, the electric potential at a point infinitely far from a charge is taken to be:
A charge of 6 mC is located at the origin. The work done in taking a small charge of -2 x 10-9 C from a point P (0, 3 cm, 0) to a Q (0,4 cm, 0) is
On moving a charge of 20 coulombs by 2 cm, 2 J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is
A charge is uniformly distributed inside a spherical body of radius r1 = 2r0 having a concentric cavity of radius r2 = r0 (ρ is charge density inside the sphere). The potential of a point P or a distance 3r0/2 from the centre is
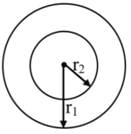
Electric field intensity at point ‘B’ due to a point charge ‘Q’ kept at a point ‘A’ is 12 NC-1 and the electric potential at a point ‘B’ due to same charge is 6 JC-1. The distance between AB is
Work done in carrying 2C charge in a circular path of radius 2m around a charge of 10C is
Dimensional formula for potential difference is
If 100 J of work has to be done in moving an electric charge of 4C from a place where potential is -5 V to another place, where potential is V volt. The value of V is
A particle of charge q1 = 3μC is located on x-axis at the point x1 = 6 cm. A second point charge q2 = 2μC is placed on the x-axis at x2 = -4 cm. The absolute electric potential at the origin is
Two spheres of radii r and R carry charges q and Q respectively. When they are connected by a wire, there will be no loss of energy of the system if
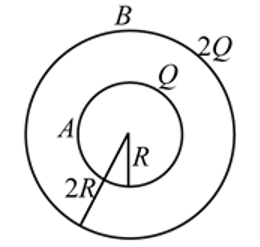
In the figure shown, conducting shells A and B have charges Q and 2Q distributed uniformly over A and B.Value of VA − VB is
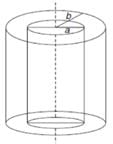
A long, hollow conducting cylinder is kept coaxially inside another long, hollow conducting cylinder of larger radius. Both the cylinders are initially electrically neutral.
The electric potential at a point (x,y) is given by: V=−Kxy. The electric field intensity a distance r from the origin varies as
Equal charges are given to two spheres of different radii. The potential will
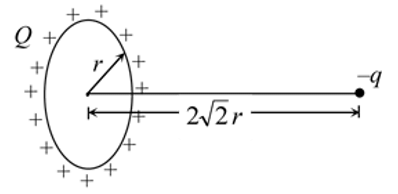
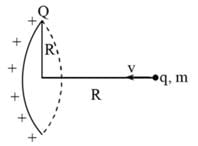
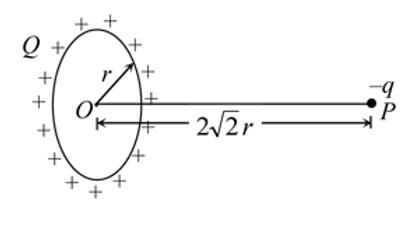
A charge −q is placed at the axis of a charged ring of radius r at a distance of 2√2r as shown in figure. If ring is fixed and carrying a charge Q, the kinetic energy of charge −q when it is released and reaches the centre of ring will be
Consider a solid cube made up of insulating material having a uniform volume charge density. Assuming the electrostatic potential to be zero at infinity, the ratio of the potential at a corner of the cube to that at the centre will be
Electric potential varies with distance such that V(x) =ax-bx3; where a and b are constants. Where will the electric field intensity be zero?
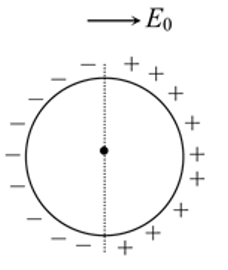
Half part of ring is uniformly positively charged and other half is uniformly negatively charged. Ring is in equilibrium in uniform electric field as shown and free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to plane. The equilibrium is


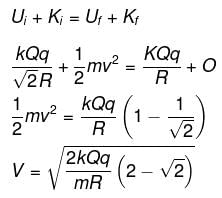


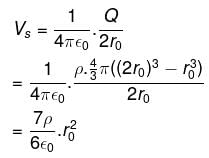
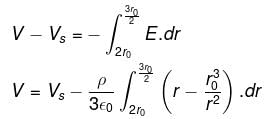
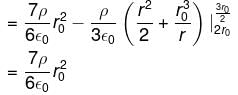
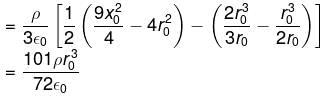
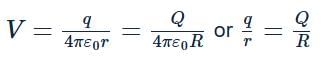
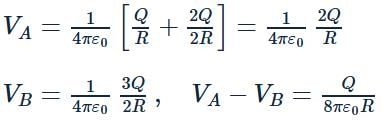
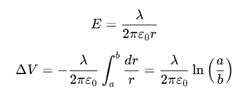
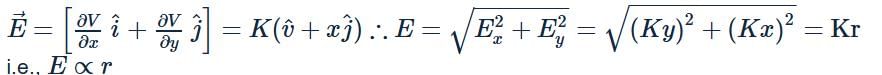
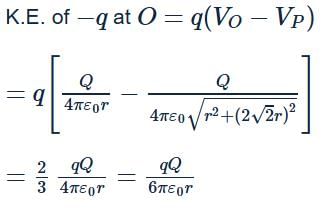


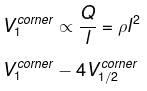
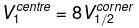
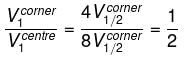
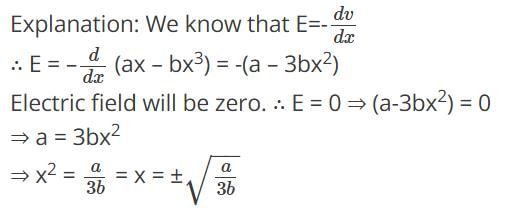
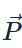 and
and 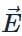 are in same direction, so potential energy U =−PE
are in same direction, so potential energy U =−PE















