NEET Part Test - 6 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Part Test - 6
A large regional unit characterised by a major vegetation type and associated fauna found in a specific climate zone constitutes:
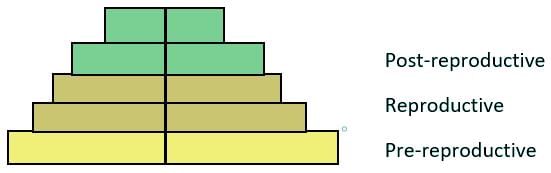
What is the population having the same number of individuals in the pre-reproductive post-reproductive age called?
Which growth pattern occurs when resources become progressively limiting in a population?
Which measure indicates the inherent potential of a population to grow?
When the number of immigration and births is more than emigration and deaths, the growth curve of the population will show
Breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes into simple forms is called?
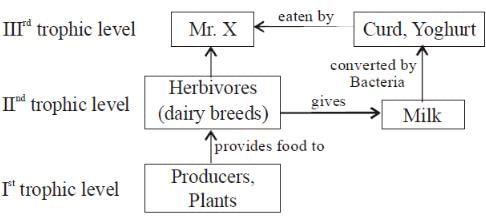
Mr. X is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Pyramids of energy and yearly biomass production can never be inverted, since this would violate the laws of thermodynamics.
(ii) Pyramids of standing crop and numbers can be inverted, since the number of organisms at a time does not indicate the amount of energy flowing through the system.
(iii) There are certain limitations of ecological pyramids such as they do not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
(iv) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
In which of the following aspect do the components of the ecosystem are seen to function as a unit?
Which one of the following aspects is not a component of functional unit of ecosystem?
Which of the following is not a factor that affects Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Introduction of Nile perch into lake victoria leads to extinction of
Which of the following group of animal is the most vulnerable to extinction