Newton's Law Of Motion NAT Level - 2 - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - Newton's Law Of Motion NAT Level - 2
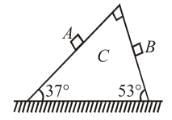
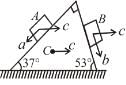
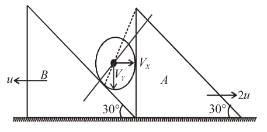
In the figure shown blocks A and B are kept on a wedge C. A, B and C each have mass m. All surfaces are smooth. Find the acceleration of C.

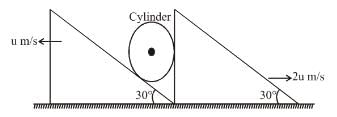
System is shown in the figure. Assume that cylinder remains in contact with the two wedges. The velocity of cylinder (in m/s) is :

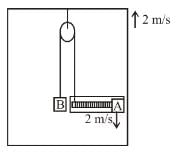
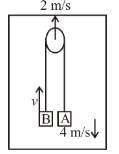
In the figure shown the velocity of lift is 2m/s while string is winding on the motor shaft with velocity 2m/s block A is moving downwards with a velocity of 2m/s, then find out the velocity of block B (in m/s).

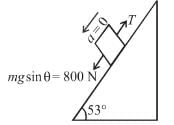
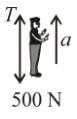
In the arrangement shown, by what acceleration (in m/s2) the boy must go up so that 100kg block remains stationary on the wedge. The wedge is fixed and friction is absent everywhere. (Take g = 10 m/s2)

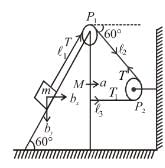
In the figures shown P1 and P2 are massless pulleys. P1 is fixed and P2 can move. Masses of A, B and C are 9m/64, 2m and m respectively. All contacts are smooth and the string is massless 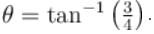 Find the acceleration of block C in m/s2.
Find the acceleration of block C in m/s2.
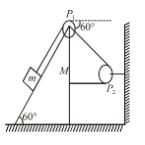
In the arrangement shown in the Figure, a block of mass m = 2 kg lies on a wedge on mass M = 8 kg. The initial acceleration of the wedge (if the surfaces are smooth) given by 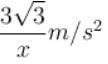 then x is.
then x is.
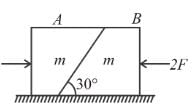
Two block A and B each of mass m are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Two horizontal force F and 2F are applied on both the blocks A and B respectively as shown in figure. The block A does not slide on block B. Then the normal reaction acting between the two blocks is nF : find the value of n.
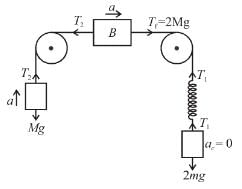
In the figure shown, the pulleys and strings are massless. The acceleration (in m/s2) of the block of mass 4m just after the system is released from rest is ...........
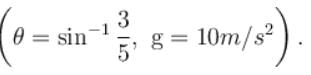
Inside a horizontally moving box, an experimenter finds that the when an object is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is released, it moves with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. In this box if 1 kg body is suspended with a light string, the tension (in N) in the string in equilibrium position. (w.r.t.) experimenter will be (Take g = 10 m/s2)
In the figure shown all the contacts are smooth. Strings and spring and light. Initially A is held by someone and B and C are at rest and in equilibrium also. Find out the acceleration of block C in m/s2 just after the block A is released. Masses of A, B and C are M, M and 2M respectively.
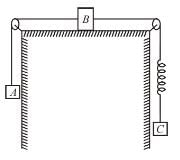



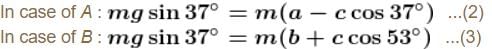
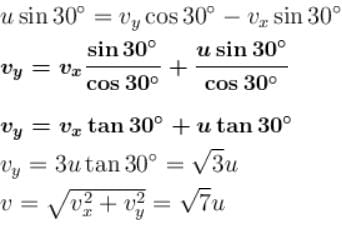

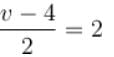
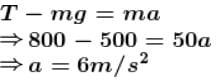
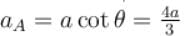 towards left.
towards left.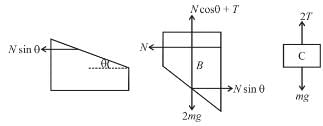

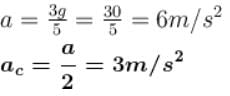


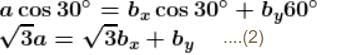

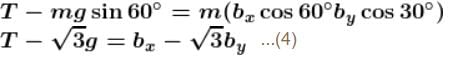
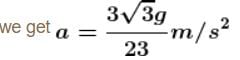
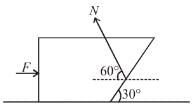
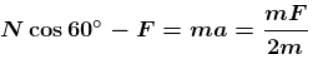
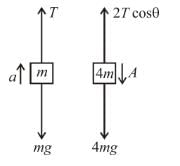

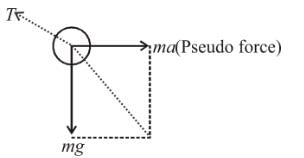

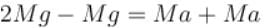 ⇒ a = g/2
⇒ a = g/2