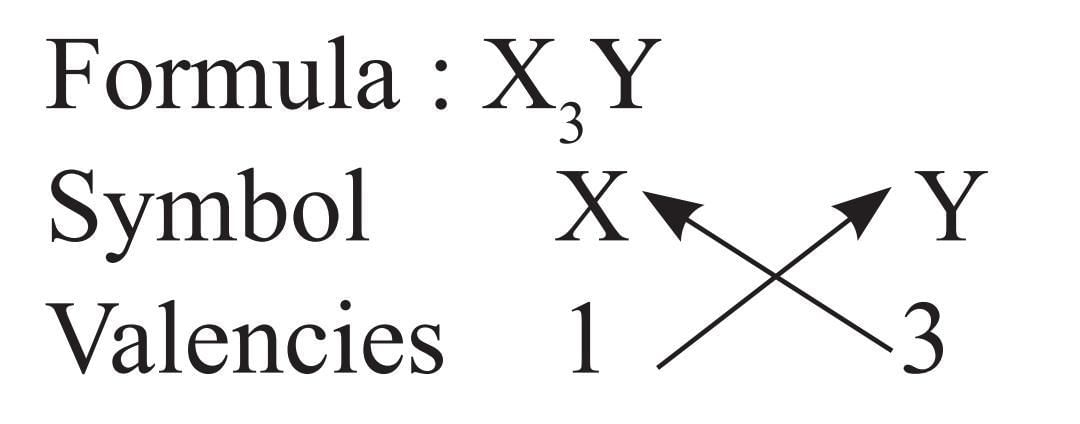Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Tests > Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Class 9 MCQ
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Class 9 MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Class 9 exam syllabus.The Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 below.
Solutions of Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for Class 9 & Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 solutions in
Hindi for Class 9 course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Class 9 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Class 9 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 1
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 2
If the number of electrons in an ion Z3– is 10, the atomic number of element Z will be
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 2
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 3
The smallest particle of a substance that is capable of independent existence is
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 3
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 4
How many litres of ammonia are present in 3.4 kg of it? (N = 14, H = 1)
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 4
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 5
Two elements X and Y has valencies of 5 and 3, & 3 and 2, respectively. The elements X and Y are most likely to be, respectively
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 5
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 6
A particle P has 18 electrons, 20 neutrons and 19 protons. This particle must be
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 7
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 8
What will be the formula mass of CaCl2 (Ca = 40, Cl = 35.5)
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 8
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 9
Molecular compounds are usually formed by combination between
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 9
Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 10
The formula of a compound is X3Y. The valencies of elements X and Y will be, respectively
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 - Question 10
Information about Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Olympiad Test: Atoms and Molecules- 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF