Olympiad Test: Dice - 2 - Class 7 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test: Dice - 2
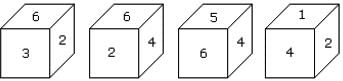
Two positions of a cube with its numbered surfaces are shown below. When the surface 4 touches the bottom, which surface will be on the top?
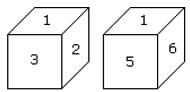

Two positions of a dice are shown below. When number ‘1’ is on the top. What number will be at the bottom?
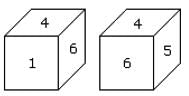

Six dice with upper faces erased are shown as:
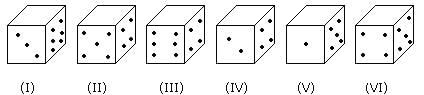
The sum of the numbers of dots on the opposite face is 7.
Q. If even numbered dice have even number of dots on their top faces, then what would be the total number of dots on the top faces of their dice?
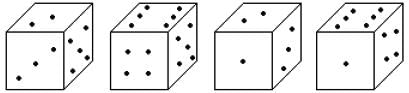
How many points will be on the face opposite to the face which contains 2 points?
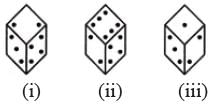
Given below are three different positions of a dice. Find the number of dots on the face opposite the face bearing 3 dots.
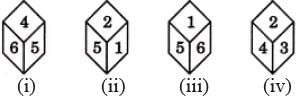
Which number is on the face opposite 4, if the four different positions of a dice are as shown in the figure given below.
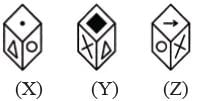
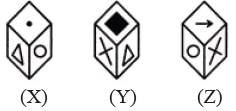
A cube has six different symbols drawn over its six faces. The symbols are dot, circle, triangle, square, cross and arrow. Three different positions of the cube are shown in figures X, Y, and Z.
Q. Which symbol occurs at the bottom of fig.(Y)?
A dice is numbered from 1 to 6 in different ways.
Q. If 1 is adjacent to 2, 4 and 6, then which of the following statements is necessarily true?