Olympiad Test Level 2: Indian Polity- 2 - Class 6 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test Level 2: Indian Polity- 2
The right provided by constitution are called
Which of the following is are included in Right to Freedom of Religion?
Which of the following are fundamental duties?
Which among the following is not among the six fundamental rights provided by Constitution?
Who was the first Chief Election Commissioner of India?
Which of the following is the federal features of the Indian constitution?
(1) Rigid constitution
(2) Appointment of Governor
(3) Integrated judiciary
(4) Bicameral legislature
Which among the following is/are NOT a requirement to be a judge of the High Court?
Match column I with Column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
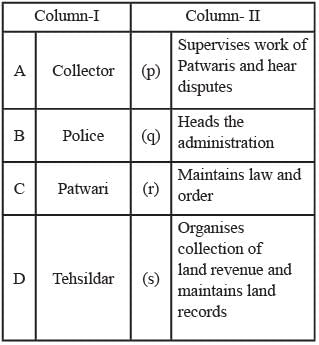
Choose the correct statements.
(1) Government can make new laws for welfare of state.
(2) Legislative Assembly approves and passes the law.
Village Panchayat is the lowest level of the three-tier Panchayat System in India. Which of the following statements is true for Village Panchayat?
Find out which the following statements are true and select the correct alternative accordingly.
(1) The RTI Act guarantees people right to hold meetings and public gatherings.
(2) Those who approach a controversial law may approach the parliament.
(3) NREGA is a scheme for mass scale employment of the rural people.
(4) Civil cases begin with the lodging of the FIR with the police.
What kind of feeling does the ballot box provide at the time of voting?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) India has a single unified and integrated judicial system.
(ii) High courts have jurisdiction over states and union territories.
(iii) Supreme court is the guardian of the constitution.
(iv) Police can keep a person in custody as long as they wish.














