Olympiad Test : Water - 2 - Grade 5 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Olympiad Test : Water - 2
When a mixture of salt + sugar + vinegar + lemon juice + soda was added into water, it resulted in the formation of a:
Water’s high surface tension allows it to do which of the following?
How many calories are absorbed/released when 1 gram of water freezes or melts?
Why doesn’t the temperature of water increase as it is undergoing a phase change?
As water vapour condenses, energy is___________and it the surrounding atmosphere.
Keerti wanted to check the solubility of some solids like sugar, salt, chalk powder, and saw dust in water. She took four beakers containing equal amount of water. Then she added the solids to each beaker, stirred the contents with a spoon and waited for some time. What did she observe?
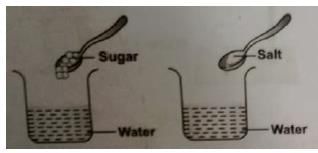
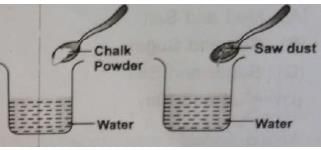
The process by which an insoluble impurity is separated from a liquid by passing the mixture through filter paper is called:
This form of water is called the purest form of water and is used in car batteries:




















