Part Test- 9 (JEE Main 2018) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Part Test- 9 (JEE Main 2018)
A cyclist is moving with a constant acceleration of 1.2 m/s2 on a straight track. A racer is moving on a circular path of radius 150 m at constant speed of 15 m/s. Find the magnitude of velocity of racer which is measured by the cyclist has reached a speed of 20 m/s for the position represented in the figure:-

In the given arrangement, n number of equal masses are connected by strings of negligible masses. The tension in the string connected to nth mass is -
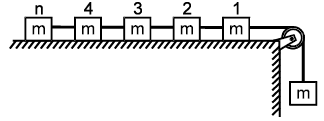
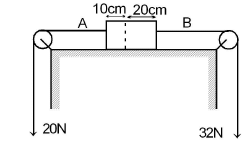
Figure shows a uniform rod of mass 3 kg and of length 30 cm. The strings shown in figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N .The acceleration of the rod is-
A balloon of mass M and a fixed size starts coming down with an acceleration f(f<g). The ballast mass m to be dropped from the ballon to have it go up with an acceleration f.Assuming negligible air resistance is find the value of m
A particle suspended from a fixed point, by a light inextensible thread of length L is projected horizontally from its lowest position with velocity . The thread will slack after swinging through an angle θ, such that θ equal
A whistle emitting a sound of frequency 440Hz is tied to a string of 1.5 m length and rotated with an angular velocity of 20 rad/sec in the horizontal plane. Then the range of frequencies heard by an observer stationed at a large distance from the whistle will be-(v = 330 m/s):
Two sound sources are moving in opposite directions with velocities v1 and v2 (v1 > v2). Bothe are moving away from a stationary observer. The frequency of both the sources is 900 Hz. What is the value of v1 – v2 so that the beat frequency observed by the observer is 6 Hz ? Speed of sound v=300m/s.Given that v1 and v2<< v :
The apparent frequency of a note is 200 Hz. When a listener is moving with a velocity of 40 ms-1 towards a stationary source. When he moves away from the same source, the apparent frequency of the same note is 160Hz. the velocity of sound in air in m/s is:
engine as heard by an observer, when the engine moves towards the observer with a speed v, is n. If the engine is stationary and the observer moves towards the engine with the same speed v, the apparent frequency of the same whistle will be :
Two periodic waves of intensities I1 and I2 pass through a region at the same time in the same direction. The sum of the maximum and minimum intensities is –
A uniformly charged rod with charge per unit length λ is bent in to the shape of a semicircle of radius R. The electric field at the centre is -
Four condensers are joined as shown in fig. the capacity of each is 8μf. the equivalent capacity
between points A and B will be -
Calculate the reading of voltmeter between X and Y then (Vx-Vy) is equal to -
A circuit is shown in the figure below. Find out the charge of the condenser having capacity 5μF
The potential difference between points A and B is -
Two bulbs 100 W, 250 V and 200 W, 250 V are connected in parallel across a 500 V line. Then-
A metal wire of mass m slides without friction on two rails spaced at a distance d apart. The track lies in a vertical uniform field of induction B, a constant current i flows along one rail, across the wire and back down the other rail. The velocity (speed and direction) of the wire as a function of time, assuming it to be at rest initially will be-
A series AC circuit has a resistance of 4? and an inductor of reactance 3?. The impedance of the circuit is z1. Now a capacitor of reactance 6? is connected in the series of above combination, the impedance becomes z2 , Then will be-
Statement I : Force between two charges decreases when air separating the charges is replaced by water.
Statement II : Medium intervening the charges has no effect on force.
Statement I : The resistance of a copper wire varies directly as the length and diameter.
Statement II : Because the resistance varies inversely the area of cross-section.
Statement I : A capacitor blocks d.c. Statement II : This is because capacitative reactance of condenser is
and for d.c. f = 0.
Image formed by a concave mirror radius of curvature 40 cm is half the size of the object.
Then distance of object and its image from the mirror will be -
An object is placed at a distance u cm from a concave mirror of focal length f cm. The real image of the object is received on a screen placed at a distance of v cm from the mirror. The values of u are changed and the corresponding values of v are measured. Which one of the graphs shown in the figure represents the variation of 1/v with 1/u ?
A ray of light enters a rectangular glass slab of refractive index √3 at angle of incidence 60º. It travels a distance of 5 cm inside the slab and emerges out of the slab. The perpendicular distance between the incident and the emergent rays is
Statement-1 : A ray incident along normal to the mirror retraces its path.
Statement-2 : In reflection, angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection
Statement I : A concave mirror is preferred to a plane mirror for shaving.
Statement II: When a man keeps his face between pole and focus of a mirror an erect and magnified virtual image is formed.
The frequency and intensity of a light source are both doubled. consider the following statements
(i) The saturation photocurrent remains almost the same
(ii)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is doubled
A photon of energy hv is absorbed by a free electron of a metal having work function ø < hv
The ionisation energies of K-shell for cobalt, copper, and molebdenum are 7.8, 9.0 and 20.1 KeV respectively. If any metal out of these is used as target in an X-ray tube operated at 15KV, then
(a) the K-series of characteristic X-rays will be emitted only by cobalt
(b) the K-series of characteristic X-rays will be emitted only by cobalt & Cu
(c) the K-series of characteristic X-rays will be emitted only by cobalt, Cu , Co and Mo
(d) the minimum wavelength of continuous X-rays emitted by the three metals will be same



















