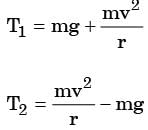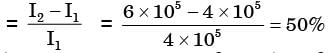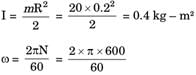Past Year Questions: Translational And Rotational Motion - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Past Year Questions: Translational And Rotational Motion
AB and CD are two uniform and identical bars of mass 10 kg each, as shown. The hinges at/A and B are frictionless. The assembly is released from rest and motion occurs in the vertical plane. At the instant that the hinge B passes the point B, the angle between the two bars will be
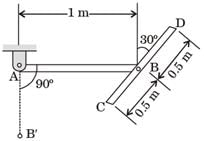
[1996]

A car moving with uniform acceleration covers 450 m in a 5 second interval, and covers 700 m in the next 5 second interval. The acceleration of the car is
[1998]
The time variation of the position of a particle in rectilinear motion is given by x = 2t3 + t2 + 2t. If v is the velocity and a is the acceleration of the particle in consistent units, the motion started with
[2005]
A simple pendulum of length of 5 m, with a bob of mass 1 kg, is in simple harmonic motion. As it passes through its mean position, the bob has a speed of 5 m/s. The net force on the bob at the mean position is
[2005]
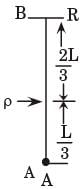
A uniform rigid rod of mass M and length L is hinged at one end as shown in the adjacent figure. A force P is applied at a distance of 2L/3 from the hinge so that the rod swings to the right. The horizontal reaction at the hinge is
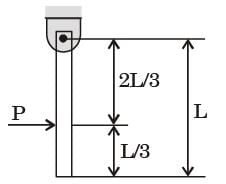
[2009]
A and B are the end points of a diameter of a disc rolling along a straight line with a counter clockwise angular velocity as shown in figure. Referring to the velocity vectors 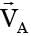 and
and 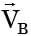 shown in the figure
shown in the figure
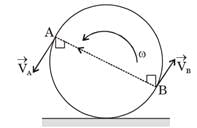
[1990]
The cylinder shown below rolls without slipping. Toward which of the following points is the acceleration of the point of contact on the cylinder directed?
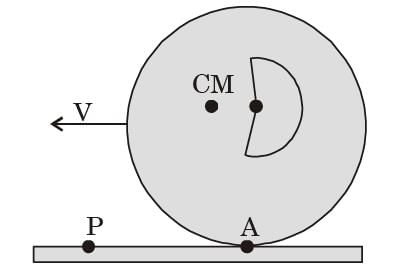
[1993]
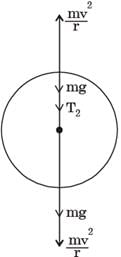
A stone of mass m at the end of a string of length l is whirled in a vertical circle at a constant speed. The tension is the string will be maximum when the stone is
[1994]
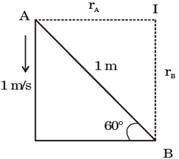
A rod of length 1 m is sliding in a corner as shown in figure. At an instant when the rod makes an angle of 60 degrees with the horizontal plane, the velocity of point A on the rod is 1 m/s. The angular velocity of the rod at the instant is
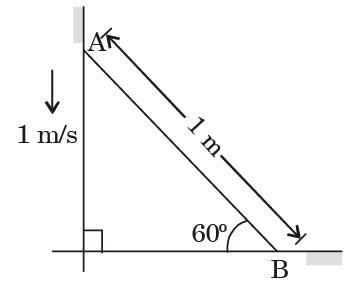
[1996]
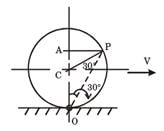
As shown in figure, a person A is standing at the centre of a rotating platform facing person B who is riding a bicycle, heading East. They relevant speeds and distances are shown in given figure person, a bicycle, heading East. At the instant under consideration, what is the apparent velocity of B as seen by A?
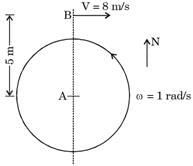
[1999]
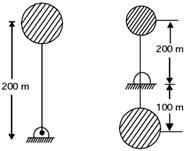
A rigid body shown in the fig. (a) has a mass of 10 kg. It rotates with a uniform angular velocity w. A balancing mass of 20 kg is attached as shown in fig. (b). The percentage increase in mass moment of inertia as a result of this addition is
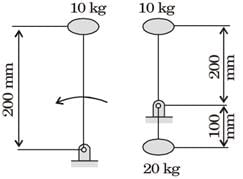
[2004]
A circular disk of a radius R rolls without slipping at a velocity V. The magnitude of the velocity at point P (see figure) is:
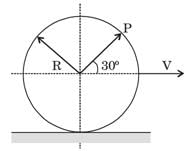
[2008]
A solid disk of radius r rolls without slipping on a horizontal floor with angular velocity ω and angular acceleration α. The magnitude of the acceleration of the point of contact on the disc is
[2012]
A circular solid disc of uniform thickness 20 mm, radius 200 mm and mass 20 kg, is used as a flywheel. If it rotates at 600 rpm, the kinetic energy of the flywheel, in Joules is
[2012]
A mobile phone has a small motor with an eccentric mass used for vibrator mode. The location of the eccentric mass on motor with respect to center of gravity (CG) of the mobile and the rest of the dimension of the mobile phone are shown. The mobile is kept on a flat horizontal surface.
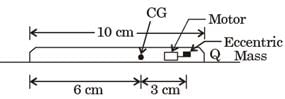
Given in addition that the eccentric mass = 2 grams, eccentricity = 2.19 mm, mass of the mobile = 90 grams, g= 9.81 m/s2. Uniform speed of the motor in RPM for which the mobile will get just lifted off the ground at the end Q is approximately
[2015]