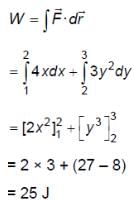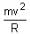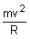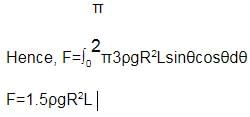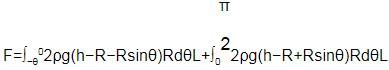Practice Test - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test
A particle experiences a variable force 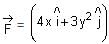 in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
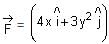 in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes by
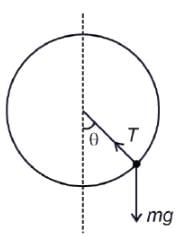
in a horizontal x-y plane. Assume distance in meters and force in newton. If the particle moves from point (1, 2) to point (2, 3) in the x-y plane; then kinetic energy changes byA stone of mass m tied to a string is being whirled in a vertical circle with a uniform speed. The tension in the string is
The length of the wire is increased by 1 mm on the application of a given load. In a wire of the same material but of length and radius twice that of the first, on application of the same force, extension produced is
Young’s modulus is defined as the ratio of longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain. Which of the following is the unit of Young’s modulus?
The volume of a spherical body is decreased by 10-3% when it is subjected to pressure of 40 atmospheres. Find the bulk modulus of body.
(1 atm = 1.01 x 105 N/m2).
Some liquid is filled in a cylindrical vessel of radius R. Let F1 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of the cylinder. Now the same liquid is poured into a vessel of uniform square cross-section of side R. Let F2 be the force applied by the liquid on the bottom of this new vessel. Then :
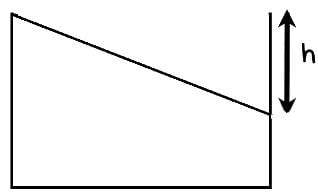
In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius R) resting on a smooth surface separates two liquids of densities 2r and 3r. The height `h' for the equilibrium of cylinder must be
An open cubical tank was initially fully filled with water. When the tank was accelerated on a horizontal plane along one of its side it was found that one third of volume of water spilled out. The acceleration was
It is now recognized that the ‘Modern Periodic Law’ is essentially the consequence of the
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer.
a. Photochemical phase occurs inside the thylakoids, especially those of grana region.
b. Biosynthetic phase reactions occur in stroma or matrix of chloroplasts and are dependent upon light.
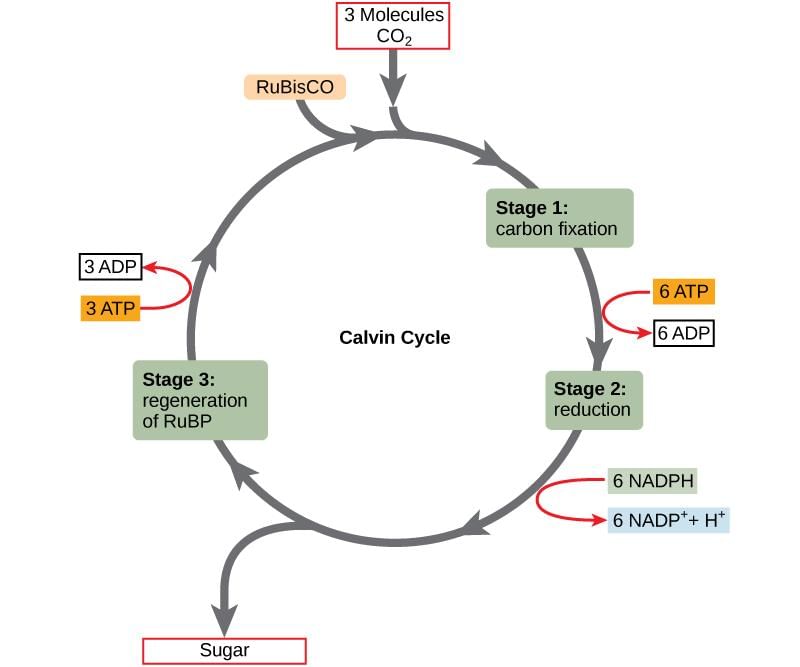
Which of the following stages of calvin cycle are in CORRECT order?
What did Jan Ingenhousz's experiments reveal about the role of sunlight in plant processes?
Electrons from exited chlorophyll molecules of photosystem II are accepted first by:
Dark fixation of CO2 in CAM plants is called ossification because it produces:
The substances that have an ability to absorb light at different specific wavelength are:
The organism which depend on the dead and decaying organic matter is:
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because:
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in:
(a) Stomata
(b) Roots
(c) Stems
(d) Lenticels
Which of the following statements are correct?
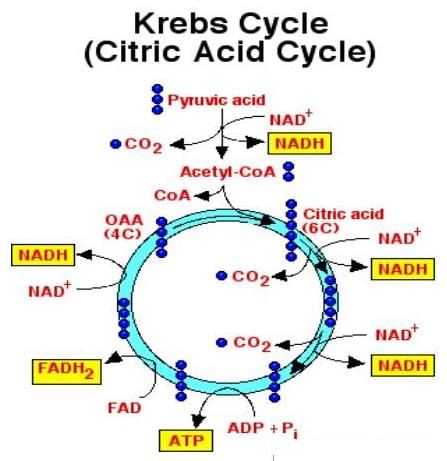
(A) The oxidation of pyruvic acid molecules formed in glycolysis occurs inside the mitochondria.
(B) Acetyl CoA is a 3-carbon compound.
(C) Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is reduced to either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
(D) Acetyl CoA molecules enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.
Which of the following reactions is catalysed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase?