Retro (Past 13 Year) JEE Main (Chemical Kinetics) - JEE MCQ
28 Questions MCQ Test - Retro (Past 13 Year) JEE Main (Chemical Kinetics)
Higher order (>3) reactions are rare due to
For the non-stoichiometric reaction,
 the following kinetic data were obtained in three separate experiments, all at 298 K.
the following kinetic data were obtained in three separate experiments, all at 298 K.
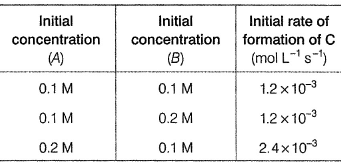
Q.
The rate law for the formation of C is
(JEE Main 2014)
The rate of a reaction double when its temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Activation energy of such a reaction will be (given,R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 and log 2 = 0.301)
(JEE Main 2013)
For a first order reaction, (A)→ products the concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 Min 40 min. The rate of reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M is
(AiEEE 2012)
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by about
(AIEEE 2011)
A reactant (A) forms two products
If then k1 and k2 are related as
(AIEEE 2011)
The time for half-life period of a certain reaction, A → products is 1 h, when the initial concentration of the reactant ‘A’ is 2.0 mol L-1. How much time does it take for its concentration to come from 0.50 to 0.25 mol L-1, if it is a zero order reaction?
(AIEEE 2010)
Consider the reaction,
Cl2(aq) + H2S(ag) → S(s) + 2H+ (aq) + 2CI- (aq)
The rate equation for this reaction is,
rate =k[Cl2] [H2S]
Q.
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation?
(AIEEE 2010)
The half-life period of a first order chemical reaction is 6.93 min. The time required for the completion of 99% of the chemical reaction will be (take, log 2= 0.301)
(AIEEE 2009)
For a reaction rate of disappearance of A is related to the rate of appearance of B by the expression
(AIEEE 2008)
Consider the reaction, 2A + B → product. When concentration of B alone was doubled, the half-life did not change. When the concentration. of A alone was doubled, the rate increased by two times. The unit of rate constant for this reaction is
(AIEEE 2007)
The energies of activation for forward and reverse reactions for are 180 kJ mol-1 and 200 kJ mol-1, respectively. The presence of a catalyst lowers the activation energy of both (forward and reverse) reactions by 100 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change of the reaction (A2 + B2 → 2 AB) in the presence of catalyst will be (in kJ mol-1)
(AIEEE 2007)
A radioactive element gets spilled over the floor of a room. Its half-life period is 30 days. If the initial activity is ten times the permissible value, after how many days will it be safe to enter the room?
(AIEEE 2007)
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO with Br2 to form NOBr
Q.
If the second step is the rate determining step, the order of the reaction with respect to NO (g) is
(AIEEE 2006)
Rate of a reaction can be expressed by Arrhenius equation as k = Ae-E/RT In this equation, E represents
(AIEEE 2006)
A reaction was found to be second order with respect to the concentration of carbon monoxide. If the concentration of carbon monoxide is doubled, with everything else kept the same, the rate of reaction will
(AIEEE 2006)
A reaction involving two different reactants can never be
(AIEEE 2005)
t1/4 can be taken as the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to drop to 3/4 of its initial value. If the rate constant for a first order reaction is k1 the t1/4 can be written as
(AIEEE 2005)
Consider an e ndotherm ic reaction X → V with the activation energies Eb and Ef for the backward and forward reactions respectively. In general
(AIEEE 2005)
The rate equation for the reaction 2A + B → C is found to be rate = k [A] [B]
The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
(AIEEE 2004)
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant, decreases from 0.8 M to 0.4 M in 15 min. The time taken for the concentration to change from 0.1 M to 0.025 M is
(AIEEE 2004)
In respect of the equation k = Ae - Ea/RT in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statements is correct?
(AIEEE 2003)
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and B is given by rate = k [A]n [B]m. On doubling the concentration of A and halving the concentration of B, the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate of the reaction will be as
(AIEEE 2003)
For the reaction system,
2NO (g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
volume is suddenly reduced to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction is of first order with respect to O2 and second order with respect to NO, the rate of reaction will
(AIEEE 2003)
For the reaction, H2 + l2 → 2HI, the differential rate law is
(AIEEE 2002)
Rate constant, k of the first order reaction when initial concentration (C0) and concentration (Ct)at time t, is given by equation kt = log C0 - log Ct Graph is a straight line, if we plot
(AIEEE 2002)
For a reaction A + 2B→ C, rate is given by + = k [A] [B], hence the order of the reaction is
(AIEEE 2002)
Consider the following two reactions,
k1 and k2 are expressed in terms of molarity (mol L-1)and time (s-1)as
(AIEEE 2002)














