SIDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test - 2 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test SIDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test Series 2025 - SIDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test - 2
Study the following statements and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding the commonly known facts.
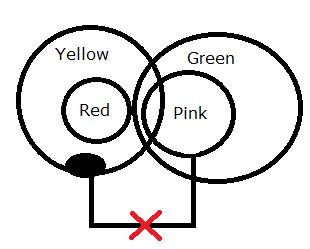
Q. Statements:
Only Yellow is red
Only a few Yellows are Pink
All pinks are green
Conclusions:
I. Some Greens are Yellow
II. All Pinks can never be red
III. No Red is Pink
Only Yellow is red
Only a few Yellows are Pink
All pinks are green
Conclusions:
I. Some Greens are Yellow
II. All Pinks can never be red
III. No Red is Pink
Study the following statements and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding the commonly known facts.
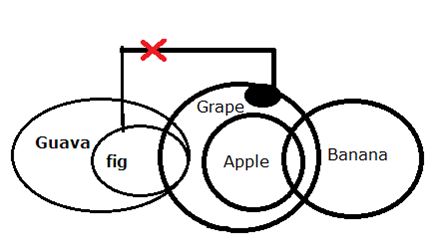
Q. Statements:
Some Apples are Bananas
All Apples are Grapes
Only a few Grapes are Figs
All Figs are Guavas
Conclusions:
I. Some Grapes are not Guavas
II. All Apples can be Bananas
III. Some Figs are Grapes
Some Apples are Bananas
All Apples are Grapes
Only a few Grapes are Figs
All Figs are Guavas
Conclusions:
I. Some Grapes are not Guavas
II. All Apples can be Bananas
III. Some Figs are Grapes
If it is possible to make only one meaningful word with the 1st, 3rd, 5th and 11th letters of the meaningful word ‘INHERITANCE’, then which would be the third letter of the word from the left? If more than one such word can be formed give ‘Y’ as the answer. If no such word can be formed, give ‘Z’ as your answer.
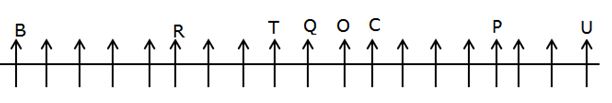
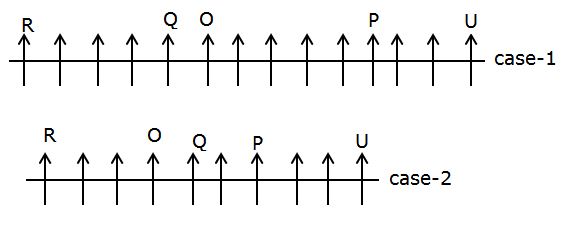
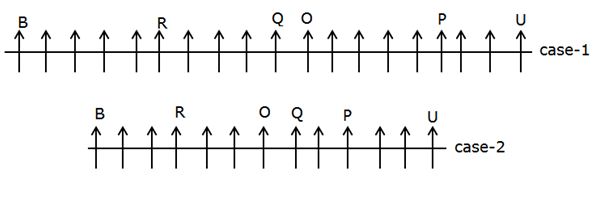
Study the following information carefully and answer the question given below:
Certain number of persons are sitting in a linear row facing towards the north.
R sits fourth to the left of Q. O is an immediate neighbor of Q. As many persons sit between O and R as between O and P. U sits third to the right of P and sits at one of the ends. The number of persons sitting to the right of U is the same as the number of persons sitting to the left of B. R sits exactly in the middle of B and O. T sits third to the left of C. Neither T nor C sits adjacent to R and P.
Q. How many persons are sitting in the row?
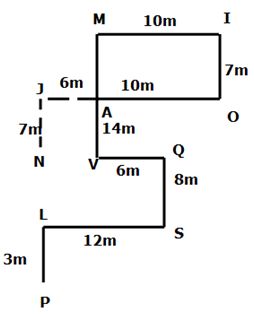
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Point L is 3m north of Point P. Point S is 8m south of Point Q which is 6m east of Point V. Point L is 12m west of Point S. Point M is 10m west of Point I which is 7m north of point O. Point V is 14m south of Point M. Point A is exactly between Point M and Point V.
If the person starts walking from Point N towards the north for 7m to reach point J, where he turns to the east and walks for 6m to reach point A.
Q. What is the distance between the points P and J?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Point L is 3m north of Point P. Point S is 8m south of Point Q which is 6m east of Point V. Point L is 12m west of Point S. Point M is 10m west of Point I which is 7m north of point O. Point V is 14m south of Point M. Point A is exactly between Point M and Point V.
If the person starts walking from Point N towards the north for 7m to reach point J, where he turns to the east and walks for 6m to reach point A.
Q. If the person from point A walks along the following points to reach point L, then how long does he walk from point A to L?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
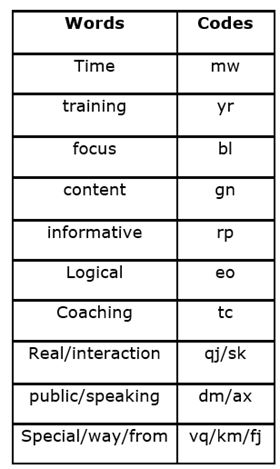
In a certain code language,
‘Real time interaction training’ means ‘yr qj mw sk’
‘Focus public speaking content’ means ‘dm ax bl gn’
‘Training informative focus time’ means ‘mw rp yr bl’
‘Logical coaching time content’ means ‘eo gn tc mw’
‘Special Way from coaching’ means ‘tc vq km fj’
Q. What is the code for the phrase ‘Informative time’ in the given code language?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a certain code language,
‘Real time interaction training’ means ‘yr qj mw sk’
‘Focus public speaking content’ means ‘dm ax bl gn’
‘Training informative focus time’ means ‘mw rp yr bl’
‘Logical coaching time content’ means ‘eo gn tc mw’
‘Special Way from coaching’ means ‘tc vq km fj’
Q. If ‘Special informative Magical way time’ is coded as ‘km fj mw rp yd’, Then what is the possible code for the phrase ‘Based from logical focus’ in the given code language?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
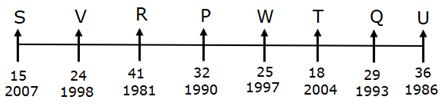
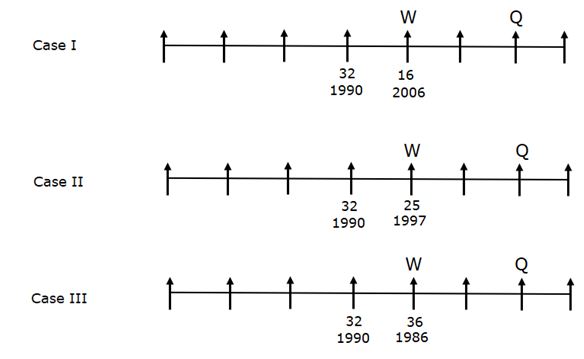
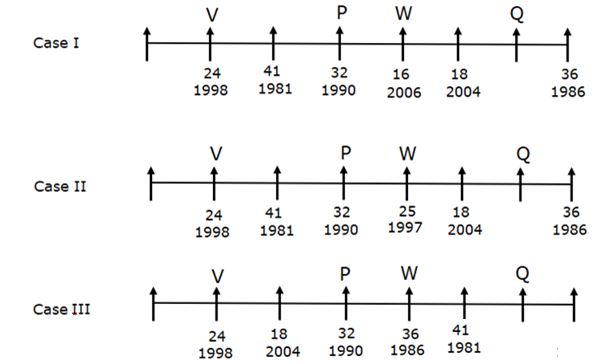
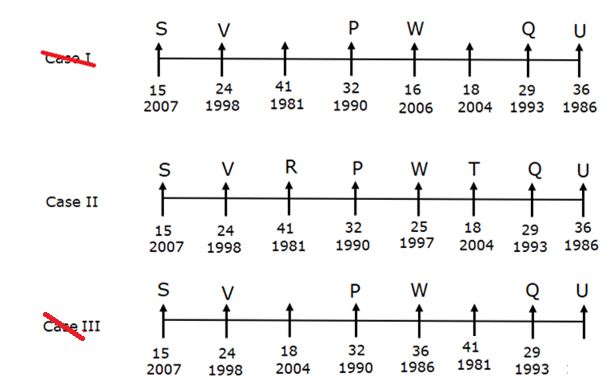
Eight persons - P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting in a linear row such that all of them are facing towards the north, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them are working in an organization with different years of experience in that organization. Their experiences are calculated based on January 2022.
Note: All the persons are joined in January of different years. The maximum and minimum experience of a person in the organization is 41yrs and 15yrs respectively.
W’s experience is a perfect square and sits second to the left of Q. The person who sits immediate right of Q is the second-most experienced person. Only three persons sit between the second-most experienced person and the person who was joined in 1990. Not more than three persons sit to the right of W. The person who has 24 years of experience sits second from the left end. V joined nine years before the one who has the least experience and sits two places away from P. The person who was joined in 2004 sits second to the left of the person who was joined in 1986. The number of persons sitting to the right of the person who has 18 years of experience is the same as the number of persons sitting to the left of the most experienced person. The person who was joined in 1993 sits adjacent to U. More than four persons sit between U and S. The difference between the experiences of S and R is one more than the experience of W.
Q. What is the position of P with respect to the one who was joined in 2007?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Eight persons - P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting in a linear row such that all of them are facing towards the north, but not necessarily in the same order. All of them are working in an organization with different years of experience in that organization. Their experiences are calculated based on January 2022.
Note: All the persons are joined in January of different years. The maximum and minimum experience of a person in the organization is 41yrs and 15yrs respectively.
W’s experience is a perfect square and sits second to the left of Q. The person who sits immediate right of Q is the second-most experienced person. Only three persons sit between the second-most experienced person and the person who was joined in 1990. Not more than three persons sit to the right of W. The person who has 24 years of experience sits second from the left end. V joined nine years before the one who has the least experience and sits two places away from P. The person who was joined in 2004 sits second to the left of the person who was joined in 1986. The number of persons sitting to the right of the person who has 18 years of experience is the same as the number of persons sitting to the left of the most experienced person. The person who was joined in 1993 sits adjacent to U. More than four persons sit between U and S. The difference between the experiences of S and R is one more than the experience of W.
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way as per the final arrangement and hence form a group. Find the one that doesn’t belong to that group.
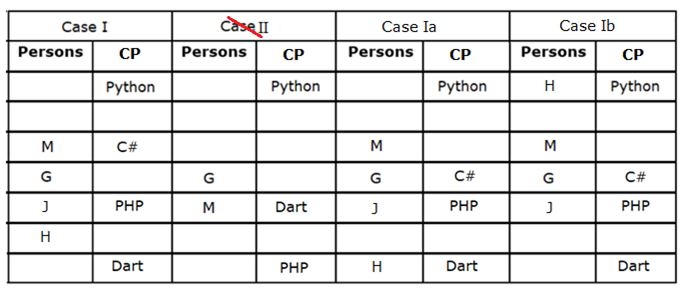
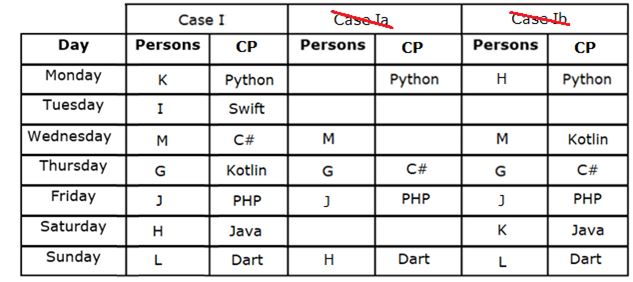
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
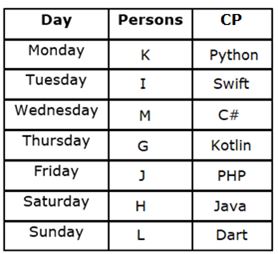
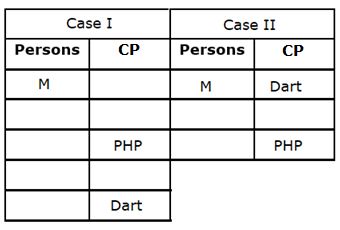
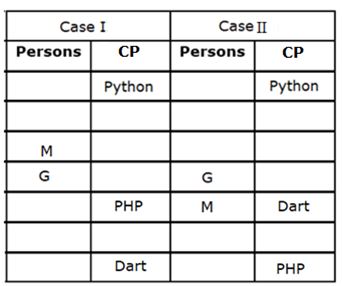
Seven persons - G, H, I, J, K, L and M participate in a hackathon held on different days of the same week starting from Monday to Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. They are expert in different Coding Programs (CP) viz. Java, Kotlin, Python, PHP, Dart, Swift and C#.
M participates two days before the one who is expert in PHP. Only one person participates between the persons who are expert in Dart and PHP. G participates three days after the one who is expert in Python, who participates before M. More than two persons participate between the persons who are experts in Python and Dart. G is not expert in PHP. Only two persons participate between H and the one who is expert in C#. The number of persons participating before G is one more than the number of persons participating after J. L participates immediately after the one who is expert in Java. As many persons participate between the one who is expert in Java and M is same as between K and the one who is expert in Kotlin. At least one persons participates between I and the one who is expert in Kotlin.
Q. How many persons participate between M and the one who participate on Saturday?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Seven persons - G, H, I, J, K, L and M participate in a hackathon held on different days of the same week starting from Monday to Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. They are expert in different Coding Programs (CP) viz. Java, Kotlin, Python, PHP, Dart, Swift and C#.
M participates two days before the one who is expert in PHP. Only one person participates between the persons who are expert in Dart and PHP. G participates three days after the one who is expert in Python, who participates before M. More than two persons participate between the persons who are experts in Python and Dart. G is not expert in PHP. Only two persons participate between H and the one who is expert in C#. The number of persons participating before G is one more than the number of persons participating after J. L participates immediately after the one who is expert in Java. As many persons participate between the one who is expert in Java and M is same as between K and the one who is expert in Kotlin. At least one persons participates between I and the one who is expert in Kotlin.
Q. Who among the following person participates three days after I?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Seven persons - G, H, I, J, K, L and M participate in a hackathon held on different days of the same week starting from Monday to Sunday, but not necessarily in the same order. They are expert in different Coding Programs (CP) viz. Java, Kotlin, Python, PHP, Dart, Swift and C#.
M participates two days before the one who is expert in PHP. Only one person participates between the persons who are expert in Dart and PHP. G participates three days after the one who is expert in Python, who participates before M. More than two persons participate between the persons who are experts in Python and Dart. G is not expert in PHP. Only two persons participate between H and the one who is expert in C#. The number of persons participating before G is one more than the number of persons participating after J. L participates immediately after the one who is expert in Java. As many persons participate between the one who is expert in Java and M is same as between K and the one who is expert in Kotlin. At least one persons participates between I and the one who is expert in Kotlin.
Q. Which of the following statement(s) is/are false with respect to the final arrangement?
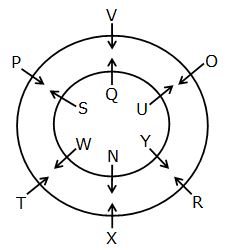
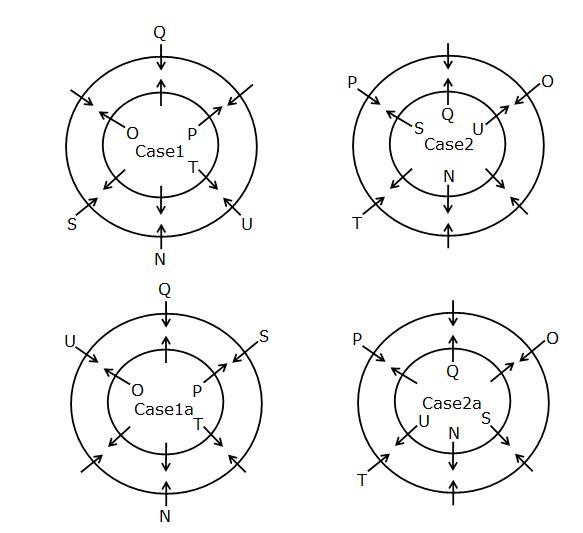
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Twelve persons N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y are sitting around two circles such that one circle is inscribed in another circle but not necessarily in the same order. The persons are sitting in the inner circle facing outside and the persons are sitting in the outer circle facing inside.
Note: If it is given that, A sits opposite to B then both A and B are sitting in the same circle i.e. either in the inner circle or in the outer circle.
N sits second to the left of the one who faces P. Q sits third to the right of N. O faces the one who is the immediate neighbour of Q. T sits opposite to O. The number of persons sits between T and O is one less than the number of persons sits between S and U when counted from the left of S. U does not sit in the same circle where P is sitting. V faces one of the immediate neighbours of S but not N. W faces the one who sits immediate left of X who does not sit in the inner circle. Y is facing R who sits opposite to P.R does not sit adjacent to W.
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group as per the given arrangement. Which of the following one does not belong to the group?
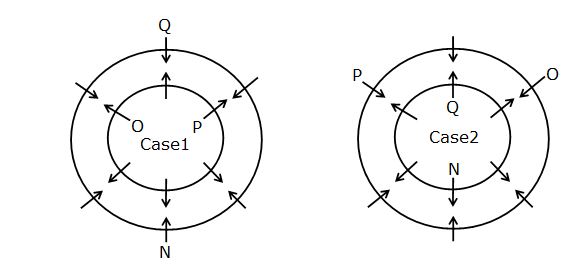
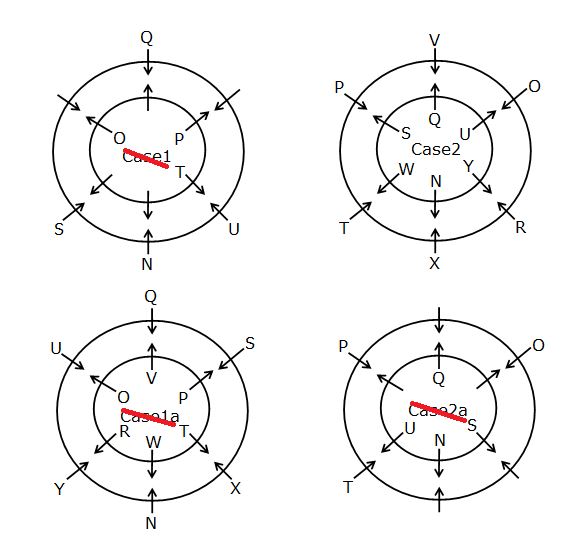
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Twelve persons N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y are sitting around two circles such that one circle is inscribed in another circle but not necessarily in the same order. The persons are sitting in the inner circle facing outside and the persons are sitting in the outer circle facing inside.
Note: If it is given that, A sits opposite to B then both A and B are sitting in the same circle i.e. either in the inner circle or in the outer circle.
N sits second to the left of the one who faces P. Q sits third to the right of N. O faces the one who is the immediate neighbour of Q. T sits opposite to O. The number of persons sits between T and O is one less than the number of persons sits between S and U when counted from the left of S. U does not sit in the same circle where P is sitting. V faces one of the immediate neighbours of S but not N. W faces the one who sits immediate left of X who does not sit in the inner circle. Y is facing R who sits opposite to P.R does not sit adjacent to W.
Q. If N is related to X and V is related to Q in a certain way, then who among the following is related to P?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Numbers and symbols arrangement machines when given an input line of numbers rearrange them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input:34568 43215 68321 57314 73196
Step I: 4562 3219 8327 7319 3194
Step II: 412 319 817 729 384
Step III: 4@2 3@9 8@7 7$9 3$4
Step IV: 04@ 36@ 01@ 08$ 01$
Step V: ##@ #&@ ##@ #&$ ##$
Step V is the last step.
Input: 69542 56832 47963 85215 49753
Q. What is the final output of “56832”?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Numbers and symbols arrangement machines when given an input line of numbers rearrange them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input:34568 43215 68321 57314 73196
Step I: 4562 3219 8327 7319 3194
Step II: 412 319 817 729 384
Step III: 4@2 3@9 8@7 7$9 3$4
Step IV: 04@ 36@ 01@ 08$ 01$
Step V: ##@ #&@ ##@ #&$ ##$
Step V is the last step.
Input: 69542 56832 47963 85215 49753
Q. What is the sum of all the numbers thus formed in step IV?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Numbers and symbols arrangement machines when given an input line of numbers rearrange them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input:34568 43215 68321 57314 73196
Step I: 4562 3219 8327 7319 3194
Step II: 412 319 817 729 384
Step III: 4@2 3@9 8@7 7$9 3$4
Step IV: 04@ 36@ 01@ 08$ 01$
Step V: ##@ #&@ ##@ #&$ ##$
Step V is the last step.
Input: 69542 56832 47963 85215 49753
Q. What is the difference between the numbers which are second from the right end and first from the left end in step II?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Thirteen alphabetical letters are arranged from left to right in such a manner to form a meaningful word. All letters are different. The word contains eight consonants and five vowels.
A is placed fourth from the right end. Only two letters are placed between A and C. The number of letters placed to the left of C is one more than the number of letters placed to the right of N. P is placed second to the right of the letter which is placed immediate left of N. Only one letter is placed between P and O. Only three letters are placed between O and M. The number of letters placed between M and A is the same as the number of letters placed between P and R. B is placed third to the left of the letter which is placed immediate right of E. B is placed neither adjacent to P nor A. E is not placed adjacent to A. T is placed fifth to the right of the letter which is placed immediate left of L. U is placed to the left of I.
Q. How many vowels are there between the letter which is third from the right end and B in the word thus formed?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Thirteen alphabetical letters are arranged from left to right in such a manner to form a meaningful word. All letters are different. The word contains eight consonants and five vowels.
A is placed fourth from the right end. Only two letters are placed between A and C. The number of letters placed to the left of C is one more than the number of letters placed to the right of N. P is placed second to the right of the letter which is placed immediate left of N. Only one letter is placed between P and O. Only three letters are placed between O and M. The number of letters placed between M and A is the same as the number of letters placed between P and R. B is placed third to the left of the letter which is placed immediate right of E. B is placed neither adjacent to P nor A. E is not placed adjacent to A. T is placed fifth to the right of the letter which is placed immediate left of L. U is placed to the left of I.
Q. What is the position of R from the left end?
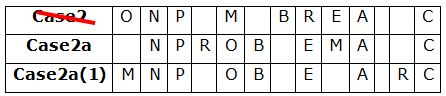
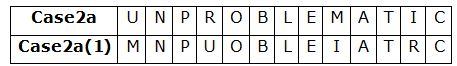
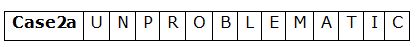
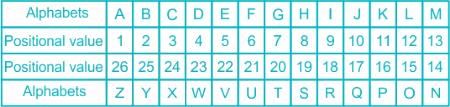
The consonants in the word 'SPLENDOR' are changed to the respective previous alphabets in the English alphabetical series and the vowels are changed to the respective alphabets succeeding them in the English alphabetical series. What is the 4th letter from the right end in the word formed after arranging the remaining letters in alphabetical order?
Direction: Read the given information and carefully answer the following questions.
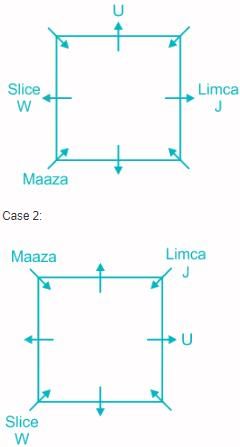
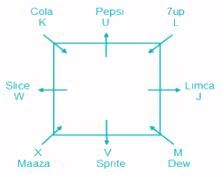
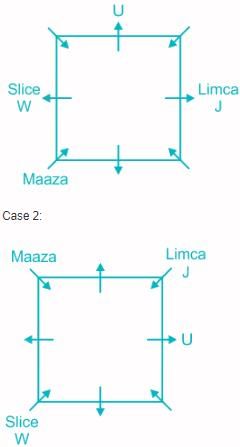
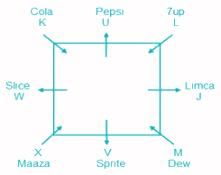
Eight people J, K, L, M, U, V, W and X are sitting around a square table but not necessarily in the same order. They all have different favorite drinks like Maaza, 7up, Slice, Dew, Sprite, Cola, Pepsi and Limca. Four of them are sitting at the corners facing towards the center and the others are sitting on each edge, facing away from the center.
L, who likes 7up, sits second to the right of M, but does not sit adjacent to the person who likes Sprite. M likes Dew and sits adjacent to V. Two people sit between J and the person who likes Maaza. W likes Slice and sits opposite to J, who likes Limca. K sits adjacent to W but does not face away from the center. V neither likes Maaza nor sits opposite to K, who likes Cola. U sits third to the left of the person who likes Maaza.
Q. Who among the following likes Pepsi?
Direction: Read the given information and carefully answer the following questions.
Eight people J, K, L, M, U, V, W and X are sitting around a square table but not necessarily in the same order. They all have different favorite drinks like Maaza, 7up, Slice, Dew, Sprite, Cola, Pepsi and Limca. Four of them are sitting at the corners facing towards the center and the others are sitting on each edge, facing away from the center.
L, who likes 7up, sits second to the right of M, but does not sit adjacent to the person who likes Sprite. M likes Dew and sits adjacent to V. Two people sit between J and the person who likes Maaza. W likes Slice and sits opposite to J, who likes Limca. K sits adjacent to W but does not face away from the center. V neither likes Maaza nor sits opposite to K, who likes Cola. U sits third to the left of the person who likes Maaza.
Q. How many people are sitting between the person who likes Maaza and L when counting from the right of L?
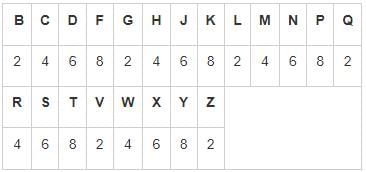
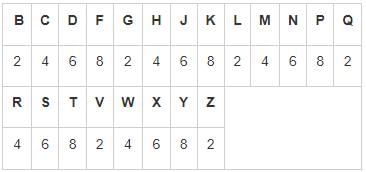
Directions: In each question below is given a group of numbers/symbols followed by five combinations of letter codes numbered (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5). You have to find out which of the combinations correctly represents the group of numbers/symbols based on the following coding system and the conditions and mark the number of that combination as your answer:
All consonants are coded one digit even numbers 2 – 8 in ascending order. For example, B is coded 2, C is coded 4 and F is coded 8. These numbers are repeated, e.g. X is coded 6, Y is coded 8 and Z is coded 2.
- If there are more than two vowels in the group of letters, then all vowels will be coded as ‘*’.
- If both the first and the last letter is a vowel, both will be coded as ‘f’.
- If the first letter is a consonant and the last letter is a vowel, both will be coded as the code for the consonant.
- If both the first and the last letter is consonant, both will be coded as ‘Ω’.
- In all the other conditions vowels are coded symbol %.
Q. Which of the following is true?
Directions: In each question below is given a group of numbers/symbols followed by five combinations of letter codes numbered (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5). You have to find out which of the combinations correctly represents the group of numbers/symbols based on the following coding system and the conditions and mark the number of that combination as your answer:
All consonants are coded one digit even numbers 2 – 8 in ascending order. For example, B is coded 2, C is coded 4 and F is coded 8. These numbers are repeated, e.g. X is coded 6, Y is coded 8 and Z is coded 2.
- If there are more than two vowels in the group of letters, then all vowels will be coded as ‘*’.
- If both the first and the last letter is a vowel, both will be coded as ‘f’.
- If the first letter is a consonant and the last letter is a vowel, both will be coded as the code for the consonant.
- If both the first and the last letter is consonant, both will be coded as ‘Ω’.
- In all the other conditions vowels are coded symbol %.
Q. What is the code for ‘HARDLY’?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
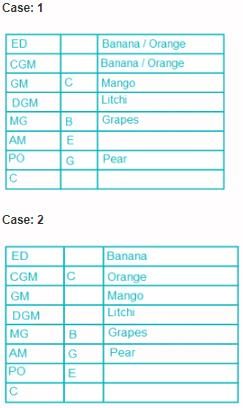
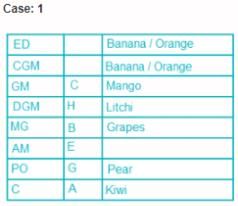
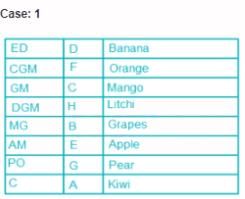
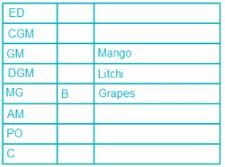
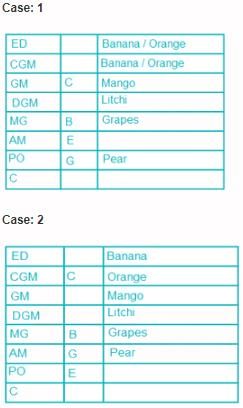
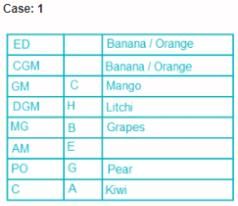
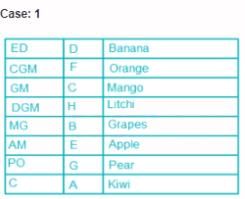
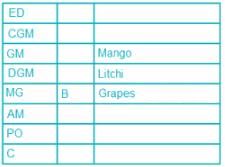
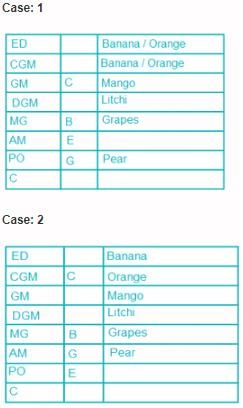
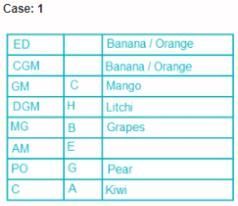
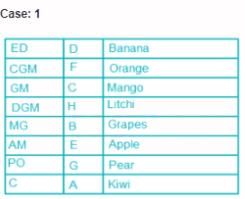
Eight people, A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H attended the party and ate different fruits Apple, Mango, Banana, Grapes, Orange, Kiwi, Litchi and Pear but not necessarily in same order. They all work in a bank and hold different positions; Clerk (C), Probationary Officer (PO), Assistant Manager (AM), Manager (MG), Deputy General Manager (DGM), General Manager (GM), Chief General Manager (CGM) and Executive Director (ED). All the positions are in increasing order where Clerk is junior to all and ED is senior to all.
G is junior to B but not junior to all and ate pear. C is junior to the one who ate banana and senior to DGM. PO did not eat apple and A ate kiwi. The person who ate orange is senior to GM. DGM ate litchi. Number of people senior to the person who ate banana is same as the number of people junior to A. B is senior to three people and ate grapes. F is not senior to everyone. The person who ate mango is junior to only two people. H is senior to B but neither ate orange nor banana. Number of people senior to C is same as number of people junior to E.
Q. Which fruit was eaten by CGM?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Eight people, A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H attended the party and ate different fruits Apple, Mango, Banana, Grapes, Orange, Kiwi, Litchi and Pear but not necessarily in same order. They all work in a bank and hold different positions; Clerk (C), Probationary Officer (PO), Assistant Manager (AM), Manager (MG), Deputy General Manager (DGM), General Manager (GM), Chief General Manager (CGM) and Executive Director (ED). All the positions are in increasing order where Clerk is junior to all and ED is senior to all.
G is junior to B but not junior to all and ate pear. C is junior to the one who ate banana and senior to DGM. PO did not eat apple and A ate kiwi. The person who ate orange is senior to GM. DGM ate litchi. Number of people senior to the person who ate banana is same as the number of people junior to A. B is senior to three people and ate grapes. F is not senior to everyone. The person who ate mango is junior to only two people. H is senior to B but neither ate orange nor banana. Number of people senior to C is same as number of people junior to E.
Q. How many people are senior to H?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Eight people, A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H attended the party and ate different fruits Apple, Mango, Banana, Grapes, Orange, Kiwi, Litchi and Pear but not necessarily in same order. They all work in a bank and hold different positions; Clerk (C), Probationary Officer (PO), Assistant Manager (AM), Manager (MG), Deputy General Manager (DGM), General Manager (GM), Chief General Manager (CGM) and Executive Director (ED). All the positions are in increasing order where Clerk is junior to all and ED is senior to all.
G is junior to B but not junior to all and ate pear. C is junior to the one who ate banana and senior to DGM. PO did not eat apple and A ate kiwi. The person who ate orange is senior to GM. DGM ate litchi. Number of people senior to the person who ate banana is same as the number of people junior to A. B is senior to three people and ate grapes. F is not senior to everyone. The person who ate mango is junior to only two people. H is senior to B but neither ate orange nor banana. Number of people senior to C is same as number of people junior to E.
Q. A is junior to how many people?
Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
Only a few A are B
Only a few B are C
Only a few C are D
Conclusions:
I. All A can be B
II. Some B are A
III. Some C are not D
Statements:
All Red is Green
All Green are White
Only a few White are Blue
Conclusions:
I. Some Red are not Green
II. No Red is Green
III. Some White are Green