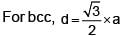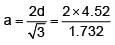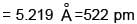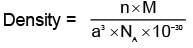Solid State & Surface Chemistry - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Solid State & Surface Chemistry
The potential difference between the fixed charged layer and the diffused layer having opposite charge is called:
Which one of the following methods is commonly used for destruction of colloid?
Select the correct statements :
(i) greater is the valency of effective ion in electrolyte more will be coagulation power of electrolyte for a given sol.
(ii) greater is the valency of effective ion in electrolyte lesser will be its coagulation value for a given sol.
(iii) peptisation is a characteristic property of colloidal solution.
(iv) micelle formation occurs only above Kraft’s temperature as well as above critical micelle concentration.
(v) lower is the gold number more is protecting power of colloid.
(i) greater is the valency of effective ion in electrolyte more will be coagulation power of electrolyte for a given sol.
(ii) greater is the valency of effective ion in electrolyte lesser will be its coagulation value for a given sol.
(iii) peptisation is a characteristic property of colloidal solution.
(iv) micelle formation occurs only above Kraft’s temperature as well as above critical micelle concentration.
(v) lower is the gold number more is protecting power of colloid.
How many ‘nearest’ and ‘next nearest’ neighbours respectively potassium have in bcc lattice?
A binary solid (A+ B-) has a zinc blends structure with B- ions constiuting the lattice and A+ ions occupying 25% tetrahedral holes. The formula of solids is:
If NaCI is doped with 10-4 mole % of SrCI2, the concentration of cation vacancies will be :
AB crystallises in a bcc lattice with edge length ‘a’ equal to 387 pm. The distance between two oppositely charged ions in the lattice is:
How many unit cells are present in a cube shaped ideal crystal of NaCI of mass 1.00 g?
[Atomic masses Na = 23, CI = 35.5]
In a compound, atoms of element Y from ccp lattice and those of element X occupy 2/3rd of tetrahedral voids. The formula of the compound will be:
Copper crystallises in fcc with a unit cell length of 361 pm. What is the radius of copper atom?
A metallic element crystallises into lattice containing a sequence of layers of ABABABAB......Any packing of spheres leaves out avpoid in the lattice. The empty space in percentage by volume on thid lattice is:
Which explains the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reversible reaction?
The unit cell length for LiCI (just like NaCI structure) is 5.14 , Assuming anion-anion contact, the ionic radius chloride ion is:
A solid XY has NaCI structure. If radius of X+ is 100 pm. What is the radius of Y- ion ?
The ionic radii of Rb+ and I- are 1.46 and 2.16 Å. The most probable type of structure exhibited by it is:
Potassium has a bcc structure with nearest neighbour distance 4.52 Å . Its atomic weight is 39, its density will be :
Addition of FeCI3 to K4[Fe(CN)6] in dilute and cold solution gives:
Isoelectric point refers to the, concentration at which the colloidal particles:
Bleeding is stopped by the application of ferric chloride. This is because:
How many tetrahedral holes are occupied in diamond?
Which of the following statements is not correct?




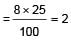
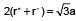
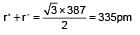

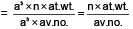
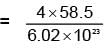 (n = 4 for cubic shape)
(n = 4 for cubic shape)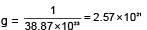
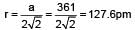
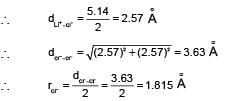
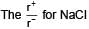 = 0.414 to 0.732 (due to fcc structure)
= 0.414 to 0.732 (due to fcc structure)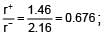 Thus, it is fcc structure or NaCI type structure.
Thus, it is fcc structure or NaCI type structure.