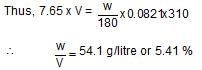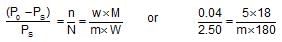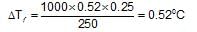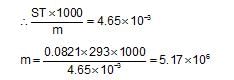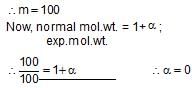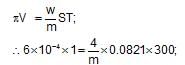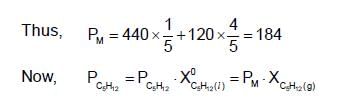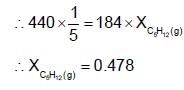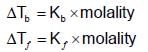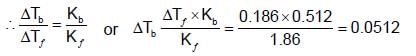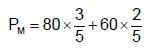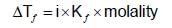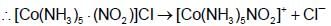Solutions - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Solutions
When a crystal of the solute is introduced into a super saturated solution of the solute:
Equimolal solutions of A and B show depression in freezing point in the ratio 2 : 1.
A remains in its normal state in solution.
B will be ...in solution
On the basis of intermolecular forces predict the correct order of decreasing boiling points of the compounds:
At high altitudes the boiling of water occurs at low temperature beacuse:
The correct relationship between the boiling points of very dilute solutions of AICI3 (t1) and CaCI2 (t2), having the same molar
concentration, is
Two solutions of KNO3 and CH3COOH are prepared separately. Molarity of both is 0.1 M and osmotic pressure are P1 and P2 respectively. The correct relationship between the osmotic pressures is:
The spontaneous movement of solute particles from a more concentrated solution is called:
The value of Kf for water is 1.860, calculated from glucose solution. The value of Kf for water calculated for NaCI solution will be:
Binary liquid solutions which exhibit negative deviations from Raoult’s law boil at temperature...than the expected value:
Which pair shows a contraction in volume on mixing along with evolution of heat:
Which characterises the weak intermolecular force of attraction in a liquid?
An aqueous solution is 1.0 molal in KI. Which undergoes dissociation in one solvent and association in other solvent is respectively:
An aqueous solution is 1.0 molal in KI,which change will cause the vapour pressure of solution to increase?
The plots of 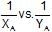 (where XA and YA are the mole fraction of liquid A in liquid and vapour phase respectively) is linear with slope and intercepts respectively:
(where XA and YA are the mole fraction of liquid A in liquid and vapour phase respectively) is linear with slope and intercepts respectively:
At 400C, the vapour pressure (in torr) of methyl alcohol (A) and ethyl alcohol (B) solution is represnted by:
P = 120 XA + 138; where XA is mole fraction of methyl alcohol. The value of lim 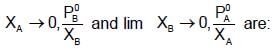
Osmotic pressure of blood is 7.65 atm at 310 K. An aqueous solution of glucose that will be isotonic with blood is ...wt./vol.
Dry air was passed successively through a solution of 5 g of a solute in 180 g of water and then through pure water. Theloss in weight of solution was 2.50 g and that of pure solvent 0.04 g. The molecular weight of the solute is:
Solute A is a ternary electrolyte and solute B is non-electrolyte. If 0.1 M solution of solute B produces an osmotic pressureof 2P, then 0.05 M solution A at the same temperature will produce an osmotic pressure equal to:
the molal elevation constant for water is 0.52 K molality-1. The elevation caused in the boiling point of water by dissolving0.25 mole of a non-volatile solute in 250 g of water will be:
Insulin (C2H10O5)n is dissolved in a suitable solvent and the osmotic pressure (p) of solutions of various concentrations(g /cm3) C is measured at 200C. The slope of a plot of π against C is found to be 4.65 x 10-3. The molecular weight of theinsulin is:
20 g of a binary electrolyte (mol.wt. = 100) are dissolved in 500 g of water. The freezing point of the solution is -0.740C, Kf= 1.86 K molality -1. The degree of ionization of the electrolyte is :
A solution containing 4 g of polyvinyl chloride in 1 litre of dioxane was found to have an osmotic pressure of 6 x 10-4 atm at 300 K. The molecular mass of the polymer is:
A solution has a 1 : 4 mole ratio of pentane to hexane. The vapour pressures of pure hydrocarbons at 200C are 440 mm Hg for pentane and 120 mm Hg for hexane. The mole fraction of pentane in vapour phase would be:
An aqueous solution freezes at -0.1860C (Kf = 1.860; Kb= 0.5120). What is the elevation in boiling point?
The vapour pressure of two liquides P and Q are 80 torr and 60 torr respectively. The total vapour pressure obtained by mixing 3 mole of P and 2 mole of Q would be:
A 0.0020 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound Co(NH3)5(NO2)CI freezes at -0.007320C. Number of moles of ions which 1 mol of ionic compound produces on being dissolved in water will be :(Kf = + 1.860C/m)


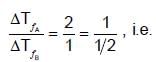 B should associate to show higher ΔT
B should associate to show higher ΔT

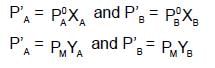
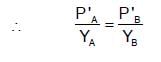
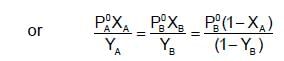
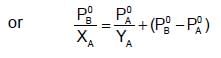
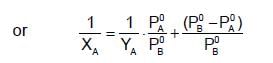
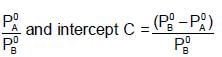
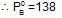 If XA = 1, then pure A
If XA = 1, then pure A 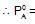 120+138=258
120+138=258