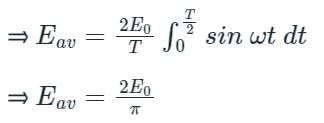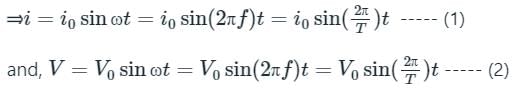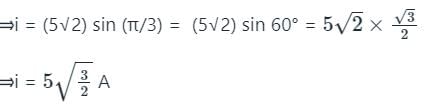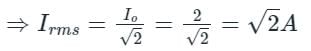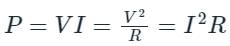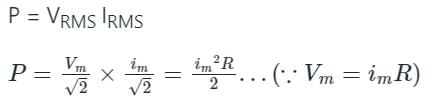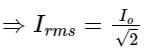Test: Alternating Current - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physics for EmSAT Achieve - Test: Alternating Current
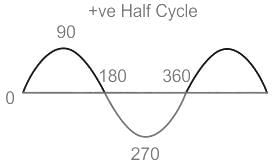
The average e.m.f. during the positive half cycle of an A.C. supply of peak value E0 is:
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is
A DC voltmeter is capable of measuring a maximum of 300 volts. If it is used to measure the voltage across a device operating at 220 volt AC supply, the reading of the voltmeter will be
Alternating current cannot be measured by d.c ammeter because:
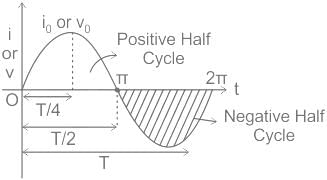
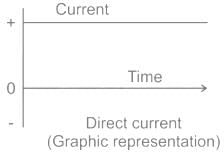
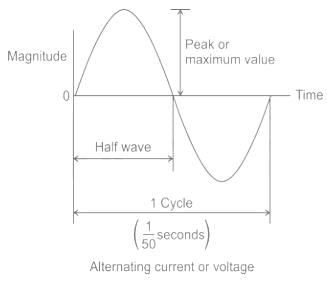
In Alternating Current (AC), the direction and magnitude of the current varies
An ac voltage v = vm sinωt applied to a capacitor drives a current in the capacitor, i = ______________.
Value of current in an A.C. circuit is I = 2cos(ωt+θ). The value of Irms is:
AC power is expressed as __________. (Where 'i'm amplitude of the AC current and 'R' is circuit resistance)
Which of the following value of current is minimum for the alternating current?
Alternating current cannot be measured by DC ammeter because:
|
215 videos|402 docs|221 tests
|