Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Tests > Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Class 10 MCQ
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Class 10 MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Atmospheric Refraction
Test: Atmospheric Refraction for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Test: Atmospheric Refraction questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Class 10 exam syllabus.The Test: Atmospheric Refraction MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Atmospheric Refraction below.
Solutions of Test: Atmospheric Refraction questions in English are available as part of our course for Class 10 & Test: Atmospheric Refraction solutions in
Hindi for Class 10 course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Atmospheric Refraction | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for Class 10 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Class 10 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 1
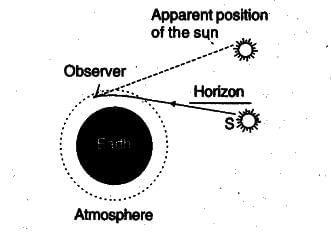
Stars appear to be higher in the sky than actually they are because of
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 1
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 2
The cold air layers of the atmosphere behave as optically
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 2
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 3
How much time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened because of atmospheric refraction ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 3
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 4
Sun appears to be risen before the actual sun rise because of
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 4
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 5
The sun can be seen before the actual sunrise by about
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 5
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 6
By how much time is the sunset delayed due to atmospheric refraction ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 6
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 7
To an observer on Earth the stars appear to twinkle. This is due to
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 7
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 8
Why does Sun appear slightly oval shaped at morning and evening ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 8
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 9
Deviation of light as it passes through the atmosphere due to variation in air density is called
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 9
Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 10
When light rays from stars enter into earth’s atmosphere, it travels from
Detailed Solution for Test: Atmospheric Refraction - Question 10
Information about Test: Atmospheric Refraction Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Atmospheric Refraction solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Atmospheric Refraction, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF