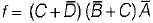Test: Boolean Algebra & Minimization Techniques- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Boolean Algebra & Minimization Techniques- 2
Consider the following statements associated with Boolean algebra:
1. There is nothing like subtraction or division in Boolean algebra.
2. There is possibility of having negative or fractional numbers.
3. A variable has no numerical significance.
4. Logical multiplication is same as the AND operation, and logical addition is the same as the OR operation. 5. There are only three constants within the Boolean system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
1. There is nothing like subtraction or division in Boolean algebra.
2. There is possibility of having negative or fractional numbers.
3. A variable has no numerical significance.
4. Logical multiplication is same as the AND operation, and logical addition is the same as the OR operation. 5. There are only three constants within the Boolean system.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Assertion (A): Boolean algebra and Binary number system are different from each other.
Reason (R): There are some basic operations like AND, OR and NOT which are performed in Boolean algebra.
Reason (R): There are some basic operations like AND, OR and NOT which are performed in Boolean algebra.
According to De Morgan’s theorem:
1. the NOR gate is equivalent to a bubbled NAND gate.
2. individual variables can be removed form under a NOT sign, and a sum of product from can be transformed to a product-of- sums form.
3. the complement of the product of variables is equal to the sum of their individual complements.
4. the NAND gate is equivalent to a bubbled NOR gate.
5. individual variables can be removed from under a NOT sign, and a product-of-sum form can be transformed to a sum-of-products form.
Q. Which of the above statements about De Morgan’s theorem is/are not correct?
1. the NOR gate is equivalent to a bubbled NAND gate.
2. individual variables can be removed form under a NOT sign, and a sum of product from can be transformed to a product-of- sums form.
3. the complement of the product of variables is equal to the sum of their individual complements.
4. the NAND gate is equivalent to a bubbled NOR gate.
5. individual variables can be removed from under a NOT sign, and a product-of-sum form can be transformed to a sum-of-products form.
Q. Which of the above statements about De Morgan’s theorem is/are not correct?
The complement of the expression 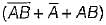 is equal to
is equal to
Match List-l (Boolean expressions)with List-ll (Minimized expression) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-l
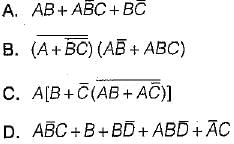
List-II
1. 0
2. B + C
3. AC + 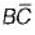
4. AB
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 3 4 1 2
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 2 3 4 1
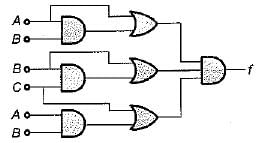
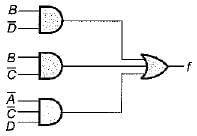
The minimized Boolean expression for the logic diagram shown below is
Assertion (A): The use of K-maps is usually limited to six-variables.
Reason (R): A K-map can not be used for problems involving more than six variables.
Assertion (A): The binary number designations of the rows and columns of the K-map are in Gray code.
Reason (R): The Gray code designation is used in K-map to ensure that two physically adjacent squares are really adjacent i.e. their minterms or maxterms differ by only one variable.
Consider the following statements:
1. The terms which cannot be combined, further in the tabular method are called “prime implicants.’’
2. The implicants which will definitely occur in the final expression are called “essential prime implicants.”
3. The prime implicant chart is a pictorial representation of the relationships between the prime implicants and the minterms of the expression.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
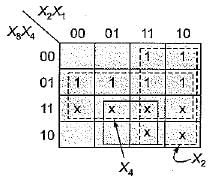
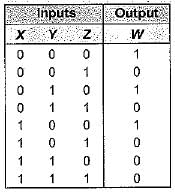
X8X4X2X1 is an 8421 BCD inputto a logic circuit whose output is 1 when X8 = 0, X4 = 0 and X2 = 1, or when X8 = 0 and X4 = 1. The simplest output of this logic circuit would be:
The inputs to a computer circuit are 4-bits of the binary number A3A2A1A0. The circuit is required to produce 1 if and only if ail of the following conditions hold.
1. The MSB is 1 or any of the other bits are 0.
2. A2 is 1 or any of the other bits are 0.
3. Any of the 4-bits are 0.
The minimized expression for the output of the computer circuit is
The minimum number of gate inputs required to implement the minimized output of the expression given by f are:
f = ∑m (1 ,5 , 6 , 12 , 13 , 14) + d(2, 4)
The minimized expression for the output given by:
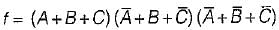
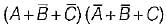
For 4 number of variables, maximum possible self dual expressions are
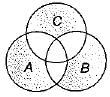
For the given Venn diagram, the minimized expression for the shaded area is
For the digital circuit shown below, the output is true if majority number of inputs are false.
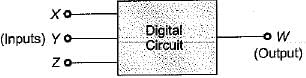
The Boolean expression for the output is given by:
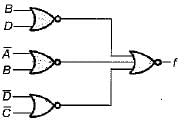
Match List-l (Logic circuit) with List-li (Output) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
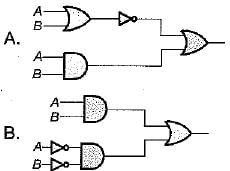
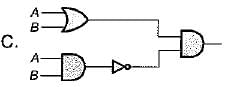
List-II
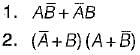
3. AB
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 3 2
(b) 1 2 1
(c) 2 1 3
(d) 2 2 1
Match List-I (Boolean expression) with List-ll (Minimized expression) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. A. (A + B)
B. AB + BC + 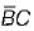
C. 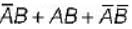
D. A + 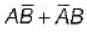
List-II
1. A + B
2. AB + C
3. A
4. 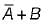
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 3 2 4 1
(b) 2 4 3 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 4 1 2
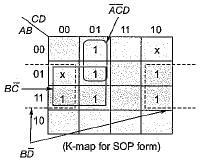
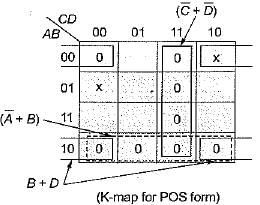
The minimized output equation of the K-map shown below has
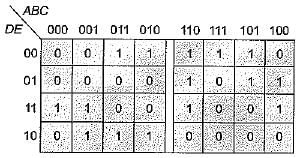
The simplified expression for the Boolean expression:
f(A, B, C, D) = ∑m (0, 2, 3, 6, 7) + ∑d (8,10,11,15) is



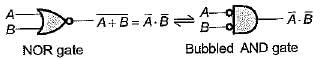 Hence, statement-1 is not correct
Hence, statement-1 is not correct Hence, statement-2 is correct.
Hence, statement-2 is correct.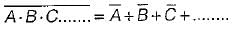 Hence, staement-3 is correct.
Hence, staement-3 is correct.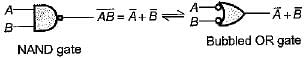 Hence, statement-4 is not correct.
Hence, statement-4 is not correct.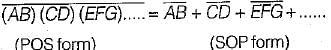 Hence, statement 5 is correct.
Hence, statement 5 is correct.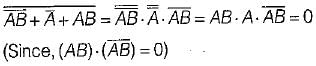
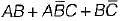
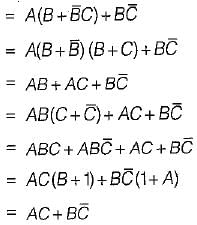
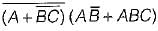
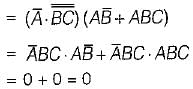
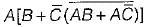
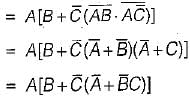
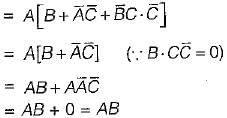
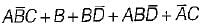
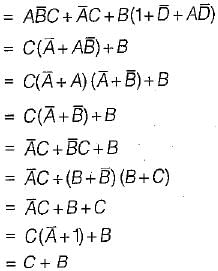
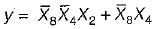
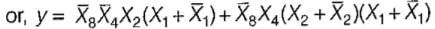
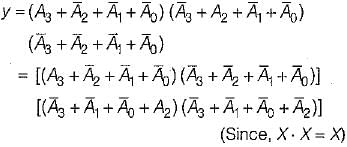
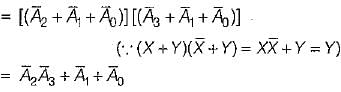
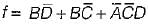
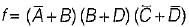
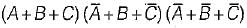
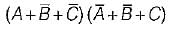

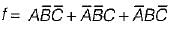
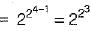
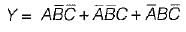
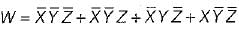
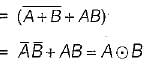
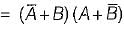
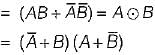
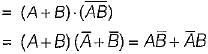
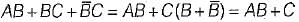
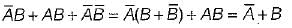
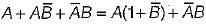 =
= 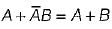
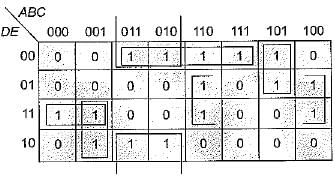
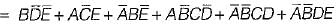
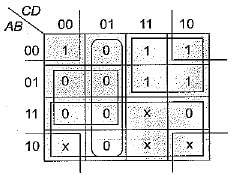
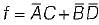 .
.