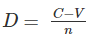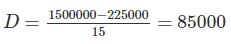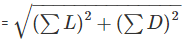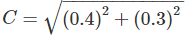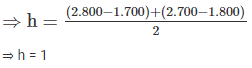Test: Civil Engineering- 1 - SSC JE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Civil Engineering- 1
For which of the following process Boucherie process is used?
Which one of the following brick is suitable for the high - class brick masonry?
The correct order of the following ingredients of Good Brick Earth with respect to its percentage composition in brick is:
Which one of the following does not belong to exogenous tree?
The defect caused due to over-maturity and unventilated storage of the wood during its transit is called:
The rough cost estimate for a building having Plinth area and Plinth area rate as 700 square meter and 9000 Rs respectively is?
Add 15 % of the estimate as additional charges for public health and electric services also.
Calculate the cost of the plastering required for a wall of 6 m long, 3.75 m high and 350 mm thick, if the rate of plastering is Rs. 17 per square meter.
Which of the following area is included in the plinth area of the building?
Find the book value of the machine at the end of 6 years if a machine is purchased for Rs. 15,00000 and has estimated life of 15 years.
Given salvage value (Rs) at the end of 15 years is 2,25,000. Use straight line method of evaluation of depreciation.
Consider the following statements:
A. Stores and Balcony are included in the calculation of carpet area.
B. Staircases within the Property unit are included in carpet area
C. Roof Terrace are excluded from the carpet area.
The correct statements are:
Accuracy in the measurement of the thickness of the slab or sectional dimension of column and beam (in centimetre) should be __________.
For 12 mm thick cement plastering 1:6 on 100 sq. m, new brick work, the quantity of cement required is _____.
Which one of the following sets of internal angles (degree) of a triangle show well condition triangle?
The staff reading at a distance of 80 m from a level with a bubble at centre is 1.31 m. When the bubble is moved 5 divisions out of the centre, the reading is 1.39 m. Then the angular value of one division of the bubble is:
If the Magnetic bearing of line is 52°40’ and magnetic declination is 4°20’ W, then the true bearing will be
Which of the following quantities are each equal to one acre?
P. 43560 sq ft
Q. 40 gunthas
R. 10 sq gunter’s chain
S. 4850 sq yds
Choose the correct answer below:
In levelling between two points A and B on opposite banks of a river, the following reading were taken:
If the R.L of A is 100.0 m, the R.L of B is
In a closed loop traverse of 1 km total length, the closing errors in departure and latitude are 0.3 m and 0.4 m respectively. The relative precision this traverse will be
Theory of error and adjustments deals with minimizing the effect of
In a solution of the three-point problem in plane table surveying, the converging of error is attained through:
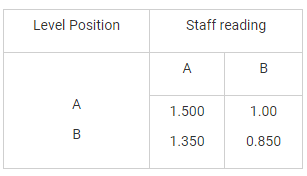
The following measurements were made during testing a levelling instrument.
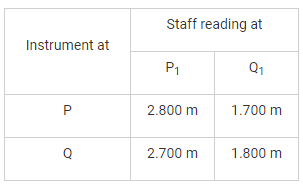
P1 is close to P and Q1 is close to Q. If the reduced level of station P is 100.00 m, the reduced level of station Q is