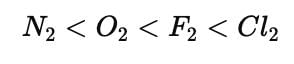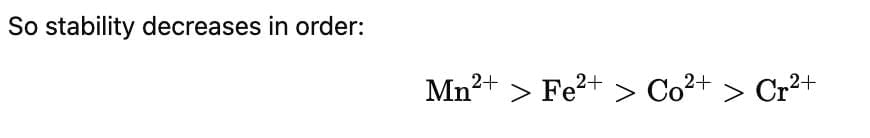Test: Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - 1
f block of the Periodic Table consists of
The elements charecterised by the filling of 4 f-orbitals, are:
14 elements after actinium is called
An element belongs to Group 15 and third period of the periodic table. Its electronic configuration will be
It is now recognized that the ‘Modern Periodic Law’ is essentially the consequence of the
Metalloids show the properties of
One of the following options is not used for explaining atomic radius
Among the alkali metals cesium is the most reactive because
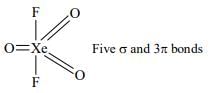
In which one of the given formulae of xenon compounds there are five σ−bonds and three π-bonds in it?
In the modern periodic table
Which of the following statements is false?
The order of Decreasing radius is
For alkali metals, which one of the following trends is INCORRECT?
Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) and the German chemist, Lothar Meyer (1830-1895) proposed arranging elements in
According to the recommendation of International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the groups in the modern periodic table are numbered from
Ionization enthalpy increases across a period because
Choose one of the following in th increasing order of bond length
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of + 2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order? (At. nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)
A transition metal ion exists in its highest oxidation state. It is expected to behave as
The sequence of ionic mobility in aqueous solution is
In the periodic table Electronegativity generally
Al(3+)<Mg(2+)<Na+<F−<O(2−)<N(3−) The above can be aptly described as
Generally, the first ionization energy increases along a period. But there are some exceptions. One which is NOT an exception is ______.
Which of the following will have the most negative electron gain enthalpy and which one the least negative? P, S, Cl, F.
For Atomic numbers greater than 100 IUPAC has made recommendation that until a new element ‘s discovery is proved, and its name is officially recognized, a systematic nomenclature be derived directly from the atomic number of the element using the numerical roots for 0 and numbers 1-9. The name 'sept' in this scheme corresponds to the digit