Test: Cognition - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Psychology and Sociology for MCAT - Test: Cognition - 1
The human brain is often described by the analogy of the brain as a computer. Which of these choices describes a possible problem with the information-processing model?
A cognitive scientist wants to test the classification of children into the correct stage of cognitive development. She recruits judges to independently score, after training, the same 30 toddlers. What is she checking for with this procedure, which tests the degree to which the judges’ scores agree?
A psychiatrist has children complete tasks to assess development. Each child is shown a three dimensional model of a mountain scene, while positioned on one side with the psychiatrist observing from the opposite side of the scene. The child is asked to look at four pictures from different viewpoints including both the child’s and the psychiatrist’s viewpoints. Nathan, one of the children from the group, looks at the 4 pictures and selects the viewpoint that matches his own.
Q. Which of Piaget’s stages of cognitive development has Nathan currently attained?
Q. Which of Piaget’s stages of cognitive development has Nathan currently attained?
Which of these would describe a person utilizing crystallized intelligence, a concept of intelligence proposed by Cattell and believed to peak in late adulthood?
Temporal monotonicity assumes that adding pain at the end of a painful experience will worsen the retrospective evaluation of the experienced pain and adding pleasure at the end will enhance the retrospective evaluation. To test this a researcher required participants to submerge one hand in cold water for one minute in the short trial. In the long trial, the participant submerged the other hand in the same temperature water for one minute, as the previous trial had required. In the long trial the participant was required to keep the hand in the water until the water temperature had raised 1o Celsius (approximately an additional 30 seconds). Afterwards, participants were asked which trial they would prefer, if required to perform another trial. A significant majority stated that they would prefer the long trial and also rated the long trial significantly less painful.
Q. Did this study’s findings support the conclusions of temporal monotonicity?
Williams syndrome, a rare neurodevelopmental disorder, is caused by a deletion from the 7th chromosome. A child with Williams syndrome has a characteristic appearance (described normally as elf-like), is extremely social, musical, shows strong linguistic skills, and displays a highly diminished amygdala response to fearful facial expressions. Williams syndrome patients were administered a version of the Preschool Racial Attitude Measure (PRAM), a typical assessment of racial and gender stereotypes. The results are shown in figure.
Q. What conclusion can be drawn regarding gender and racial bias in decision making based on this study?
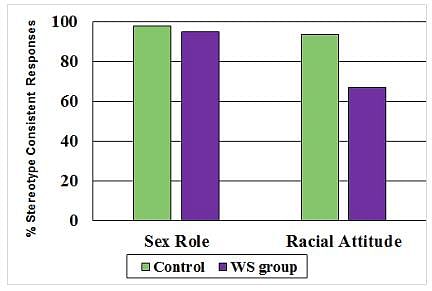
The percentage of responses showing stereotype-consistent bias in children with Williams syndrome (WS) and control children.
Attribution: Santos, A., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., & Deruelle, C. (2010). Absence of racial, but not gender, stereotyping in Williams syndrome children. Current Biology, 20(7), R307-R308.
What term describes the phenomenon in which new information interferes with the ability to recall previously learned information?
|
339 videos|14 docs|42 tests
|




















