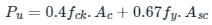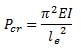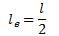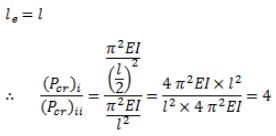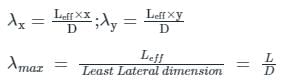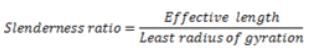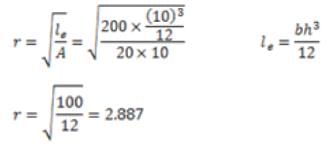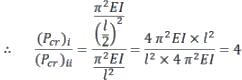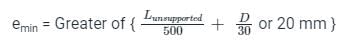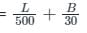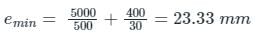Test: Columns - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Columns
As per IS 456 ∶ 2000, short axially loaded RC column members using mild steel are des by the equation
where,
Pu = factored axial load on the member
fck = characteristic compressive strength of the concrete
fy = characteristic strength of the compression reinforcement
Ag = gross cross sectional area
Ac = area of concrete
Asc = area of longitudinal reinforcement of column
where,
Pu = factored axial load on the member
fck = characteristic compressive strength of the concrete
fy = characteristic strength of the compression reinforcement
Ag = gross cross sectional area
Ac = area of concrete
Asc = area of longitudinal reinforcement of column
The ratio of Euler’s buckling loads of column with the same parameters having (i) both ends fixed, and (ii) both ends hinged is
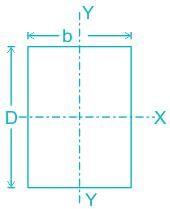
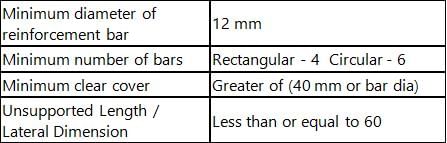
Select the CORRECT name of the column among the given options that should have the ratio of effective length to its least lateral dimension more than 12.
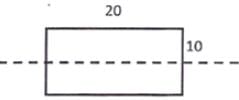
A column has a rectangular cross-section of 10 mm20 mm and a length of 1 m. The slenderness ratio of the column is close to
A short axially loaded square column 500 mm × 500 mm is subjected to service load of 2000 kN. Calculate the ultimate load and minimum area of longitudinal reinforcement as per IS 456:2000
For a long slender column of uniform cross section, the ratio of critical buckling load for the case with both ends clamped to the case with both ends hinged is
The limits of percentage 'P' of the longitudinal reinforcement in a column is given by
The minimum eccentricity to be considered for an axially loaded RCC column of size 400 mm × 400 mm with unsupported length of 5 m is:
According to IS 456 : 2000, the minimum and maximum percentage of longitudinal reinforcement in a column (expressed as percentage of gross cross-sectional area of the column), are respectively:
A reinforced concrete column of size 400 mm × 400 mm is having the diameter of longitudinal bar as 20 mm. The pitch of lateral ties in such a case should be: