Test: Common Diseases in Humans & Immunity - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Common Diseases in Humans & Immunity
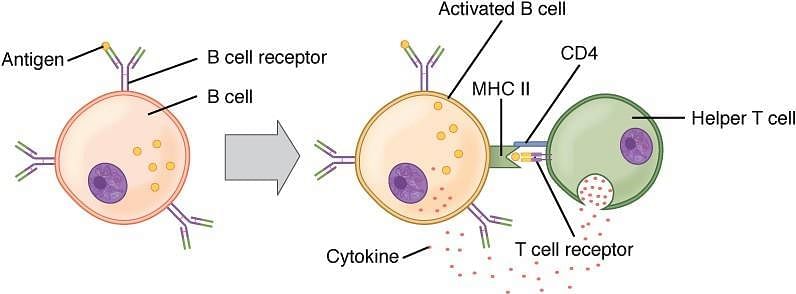
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:
Which lymphoid organ reduces in size as an individual ages and becomes quite small by the time of puberty?
The disease chikungunya is transmitted by:
Anti venom against snake poison contains:
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in_________.
How are Infectious Diseases transmitted?
Assertion (A): Malaria is caused by a virus.
Reason (R): Malaria is transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to:
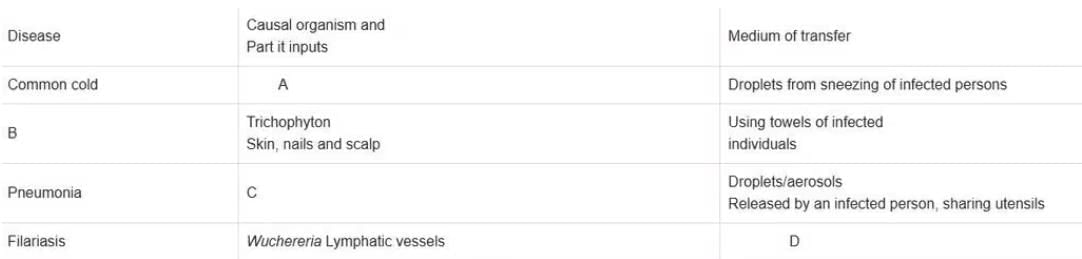
Fill in the blanks in the different columns of the table given below
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium: