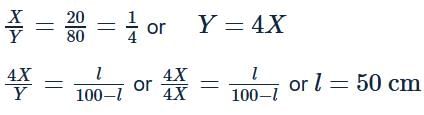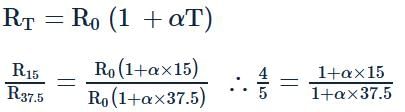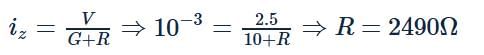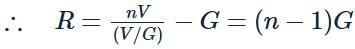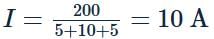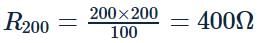Test: Current Electricity - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Current Electricity - 1
The Wheatstone bridge is balanced for four resistors R1,R2,R3 and R4 with a cell of emf 1.46 V. The cell is now replaced by another cell of emf 1.08 V. To obtain the balance again
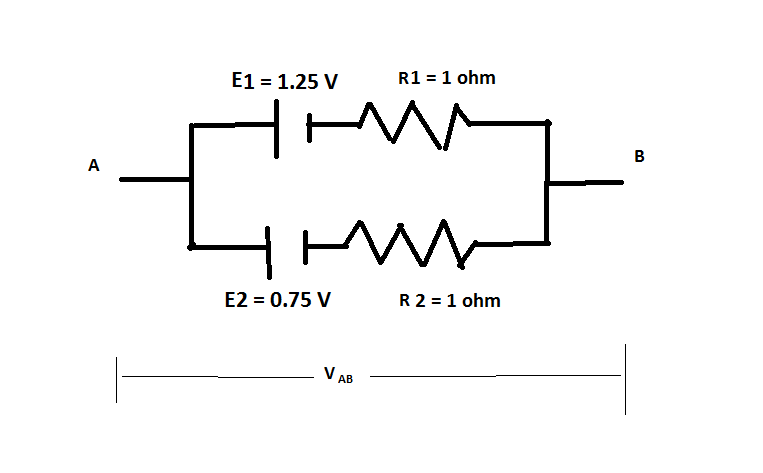
Two cells of emf 1.25V , 0.75V and each of internal resistance 1Ω are connected in parallel. The effective emf will be
If the length of the filament of a heater is reduced by 10% the power of the heater will
A cylindrical wire of radius R has current density varying with distance r from its axis as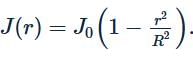 The total current through the wire is
The total current through the wire is
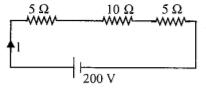
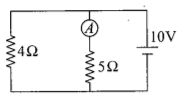
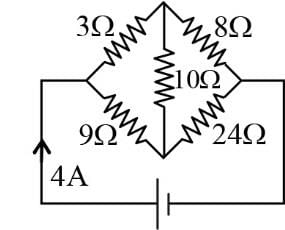
In the circuit shown in Fig., the reading of the ammeter is (assume internal resistance of the battery to be zero)
Drift is the random motion of the charged particles within a conductor,
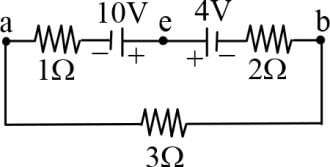
In the circuit diagram shown below, the magnitude and direction of the flow of current, respectively, would be
In a metre bridge experiment, null point is obtained at 20 cm from one end of the wire when resistance X is balanced against another resistance Y. If X<Y, then where will be the new position of the null point from the same end, if one decides to balance a resistance of 4X against Y ?
Potentiometer measures the potential difference more accurately than a voltmeter, because
The ratio of the resistance of conductor at temperature 15°C to its resistance at temperature 37.5°C is 4:5 . The temperature coefficient of resistance of the conductor is -
The resistance of a galvanometer is 10Ω. It gives full-scale deflection when 1 mA current is passed. The resistance connected in series for converting it into a voltmeter of 2.5 V will be
A piece of copper and another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 80K. The resistance
A milliammeter of range 10 mA has a coil of resistance 1 Ω. To use it as an ammeter of range 1 A, the required shunt must have a resistance of
In the circuit shown, if the 10 Ω resistance is replaced by 20 Ω, then the amount of current drawn from the battery will be
In a potentiometer experiment, for measuring internal resistance of a cell, the balance point has been obtained on the fourth wire. The balance point can be shifted to fifth wire by
A voltmeter has a resistance of G ohm and range V volt. The value of resistance used in series to convert it into voltmeter of range nV volt is
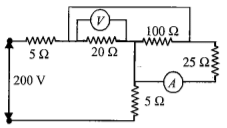
In the figure, voltmeter and ammeter shown are ideal. Then voltmeter and ammeter readings, respectively, are
The operating temperature of the filament of lamp is 2000∘C. The temperature coefficient of the material of filament is 0.005∘C−1. If the atmospheric temperature is 0∘C, then the current in the 100 W, 200 V rated lamp when it is switched on is nearest to
Three identical cells, each having an e.m.f. of 1.5 V and a constant internal resistance of 2.0Ω, are connected in series with a 4.0Ω resistor R, first as in circuit (i), and secondly as in circuit (ii).
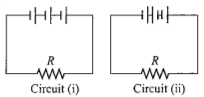
What is the ratio 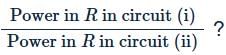
The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by:
Three similar light bulbs are connected to a constant voltage d.c. supply as shown in Fig. Each bulb operates at normal brightness and the ammeter (of negligible resistance) registers a steady current.
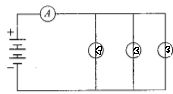
The filament of one of the bulbs breaks. What happens to the ammeter reading and to the brightness of the remaining bulbs?
Ammeter reading _______ & Bulb brightness _______
In a meter bridge experiment a balance point is obtained at a distance of 60 cm from the left end when unknown resistance R is in a left gap and 8 ohms resistor is connected in the right gap. When the position of R and 8 ohm resistor is interchanged the balance point will be at distance of
|
90 videos|435 docs|88 tests
|