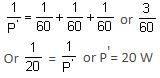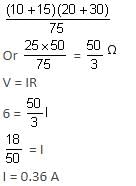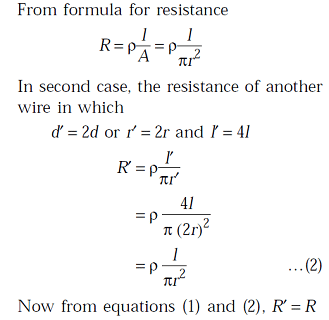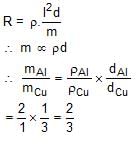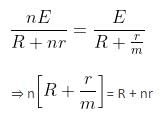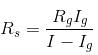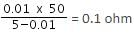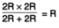Test: Current Electricity - 2 - CUET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Current Electricity - 2
When three identical bulbs of 60 W, 200 V rating are connected in series to a 200 V supply, the power drawn by them will be
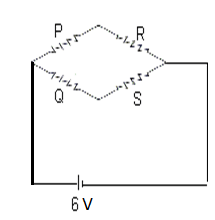
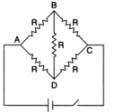
In the network given, P = 10Ω, Q = 20Ω, R = 15Ω, S = 30Ω and voltage = 6V. The current passing through the battery (of negligible internal resistance) is
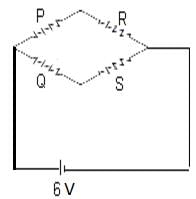

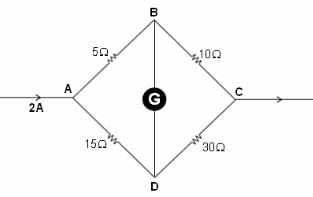
For the wheatstone bridge shown in the figure, total current is 2 A. What will be the current through BD?
Which of the following ways is/are correct to increase current in the circuit?
- Decrease the voltage while decreasing the resistance.
- Increase the voltage while holding the resistance constant.
- Decrease the resistance while holding the voltage constant.
- Increase the voltage while increasing the resistance.
- Raise the voltage, but only if you raised the resistance by same factor.
An electric bulb is rated 220 volt - 100 watt. What will be the power consumed by it when operated on 110 volt?
The resistance of wire of uniform diameter d and length l is R. The resistance of another wire of the same material, but diameter 2d and length 4l will be
An aluminium rod and a copper rod have the same length and resistance. The specific resistance of copper is half of aluminium, but its density is thrice of aluminium. What will be the ratio of the mass of aluminium rod to the mass of copper rod?
The resistance of a bulb filament is 100 Ω at a temperature of 100°C. If its temperature coefficient of resistance is 0.005 per °C, then its resistance will become 115 Ω at a temperature of
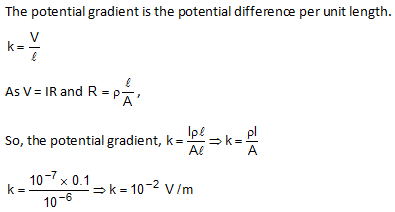
A potentiometer has uniform potential gradient. The specific resistance of the material of the potentiometer wire is 10-7 ohm-metre, and the current passing through it is 0.1 ampere, cross-section of the wire is 10-6m2. The potential gradient along the potentiometer wire is
Two batteries, one of emf 18 V and internal resistance 2Ω and the other of emf 12 V and internal resistance 1Ω, are connected as shown. The voltmeter V will record a reading of

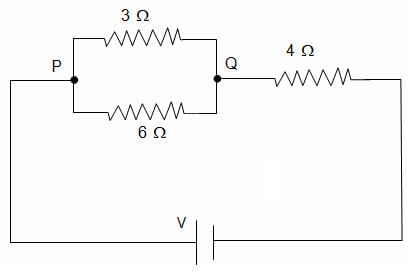
If the current through 3 Ω resistor is 0.8 A, then the potential drop through 4 Ω resistor is
Two identical cells, whether connected in parallel or in series, give the same current when connected to an external resistance of 1.5Ω. Find the value of internal resistance of each cell.
The resistance of a galvanometer is 50 Ω. When 0.01 A current flows in it, full scale deflection is obtained in the galvanometer. The resistance of shunt connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of range 5 A will be
In a Wheatstone bridge, all the four arms have equal resistance R. If the resistance of the galvanometer arm is also R, the equivalent resistance of the combination as seen by the battery is