Test: Differential Equations Of Physical Systems And Dynamics Of Robotic Mechanisms - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Differential Equations Of Physical Systems And Dynamics Of Robotic Mechanisms
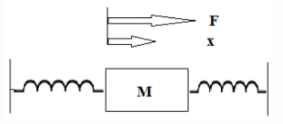
Consider a simple mass spring friction system as given in the figure K1, K2 are spring constants f-friction, M-Mass, F-Force, x-Displacement. The transfer function X(s)/F(s) of the given system will be :
The output of an first order hold between two consecutive sampling instants is:
Which of the following is an example of an open loop system?
A tachometer is added to servomechanism because:
A synchro Transmitter is used with control transformer for:
The below figure represents:
Backlash in a stable control system may cause:
Tachometer feedback in a D.C. position control system enhances stability?
For a tachometer, if a(t) is the rotor displacement, e(t) is the output voltage and K is the tachometer constant, then the transfer function is given by:
Gear train in the motor is used to reduce the gear ratio?
Assertion (A): Servomotors have heavier rotors and lower R/X ratio as compared to ordinary motors of similar ratings.
Reason (R): Servomotor should have smaller electrical and mechanical time constants for faster response.
Assertion (A): DC servomotors are more commonly used in armature controlled mode than field controlled mode.
Reason (R): Armature controlled Dc motors have higher starting torque than fiels controlled motors.
In case of DC servomotor, the back emf is equivalent to an “electric friction” which tends to:
The lagrangian is defined as:
A gantry robot consists of a manipulator mounted on an overhead system that allows movement only in ________ plane.














