Test: Digital Electronics - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Digital Electronics - 1
In a certain digital waveform, the period is four times the pulse width. The duty cycle is ________.
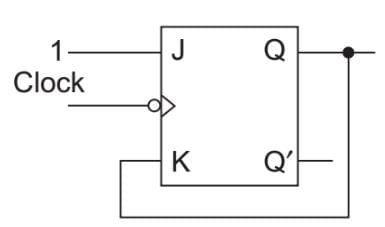
For the circuit shown below, Q = 0 initially. What shall be the subsequent states of Q when clock pulses are given?

Which of the following operation are performed on linear queues?
- Testing a linear queue for underflow
- Enqueue operation
- Dequeue operation
- Testing a linear queue for overflow.
If Vin is 0.99 V, what is the digital output of the ADC0801 after INTER goes low?
Assertion (A): Hamming code is commonly used for error correction
Reason (R): In Hamming code the number of parity bits increases as the number of information bits increases.
A microcomputer has memory locations from 0000 to FFFF, each storing 1 byte. How many bytes can be the memory store?
A clock signal coordinates the working of different flip flops.
In 8085, usually the vector location and the next two memory location contain a JMP instruction. This allows the programs to branch to
In a positive-edge-triggered JK flip-flop, a low J and a low K produce __________ state. A high __________ on the rising edge of the clock.
The rate of change of digital signals between High and Low level is
Which of the following is best suited for parity checking and parity generation?
In the circuit shown below, the outputs Y1 and Y2 for the given initial condition Y1 = Y2 = 1 and after four input pulses will be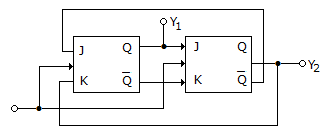
Assertion (A): Power drain of CMOS increases with operating frequency
Reason (R): All unused CMOS inputs should be tied either to a fixed voltage level (0 or VDD) or to another input.
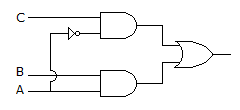
For the logic circuit of the given figure the simplified Boolean expression is
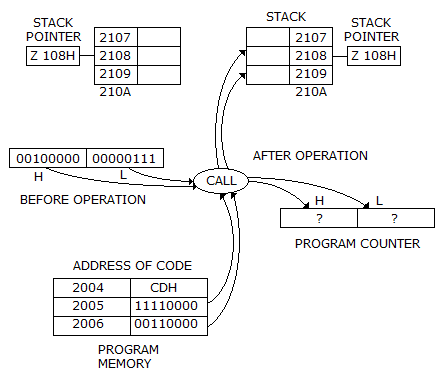
The contents of stack location 2109 H after the call operation will be