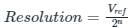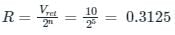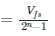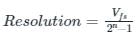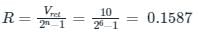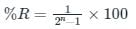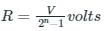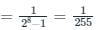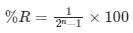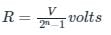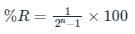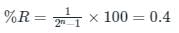Test: Digital to Analog Converters - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Digital to Analog Converters
Given below are three types of converters
- successive approximation type
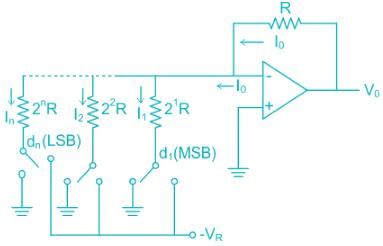
- weighted resistor type
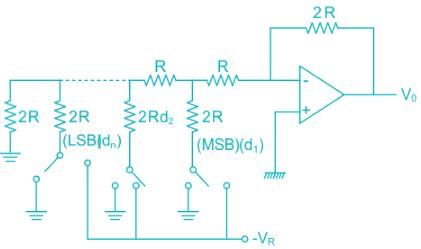
- R-2R ladder type
Q. Which one of the types are D to A converter?
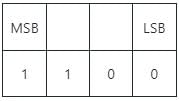
Identify the most significant bit from the '100010' binary data.
Two 10-bit ADCs, one of successive approximation type and other of single slope integrating type, take Ta and Tb time respectively to convert 3V analog input signal to digital output. If the input analog signal is increased to 6V, the approximate time taken by the two ADCs will respectively be
The smallest change in the input signal that can be detected by an instrument is called
A 5 bit ladder has a digital input of 11010. Assuming that 0 corresponds to 0 V and 1 corresponds to +10 V, its output voltage will be:
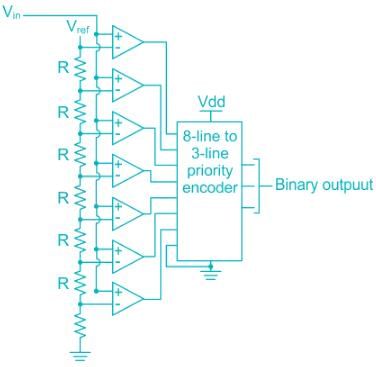
Which of the following is the fastest A-D converter?
A 6-bit ladder D/A converter has a maximum output of 10 V. The output for input 101001 is approximately
The difference between analog voltage represented by two adjacent digital codes of an analog to digital converter is
If the resolution of a digital-to-analog converter is approximately 0.4% of its full-scale range, then it is a/an _______.