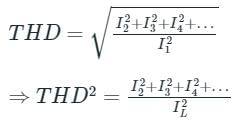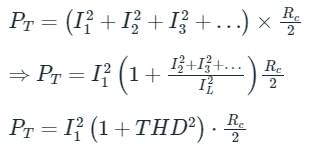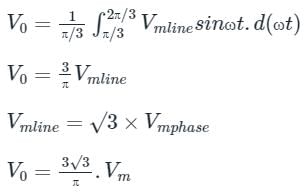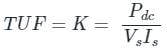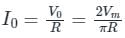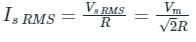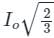Test: Diode Rectifiers - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Diode Rectifiers
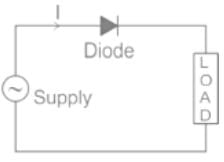
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions' is a perfect example of:
In comparing the operation of the half-controlled 2-pulse circuit with that of the fully-controlled circuit, which of the following statements are evident?
1. Since half the thyristors are replaced by diodes, a half-controlled converter costs less than a fully-controlled converter.
2. Due to the freewheeling action with a half-controlled bridge-circuit power factor is improved in half-controlled converters.
3. The AC supply current is more distorted due to its zero periods with the half-controlled circuit, compared to a fully-controlled bridge circuit.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
2. Due to the freewheeling action with a half-controlled bridge-circuit power factor is improved in half-controlled converters.
3. The AC supply current is more distorted due to its zero periods with the half-controlled circuit, compared to a fully-controlled bridge circuit.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
The average current rating of a semiconductor diode will be maximum for:
For a total harmonic distortion of 0.1 with I1 = 4A and Rc = 8Ω, calculate total power
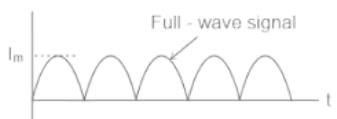
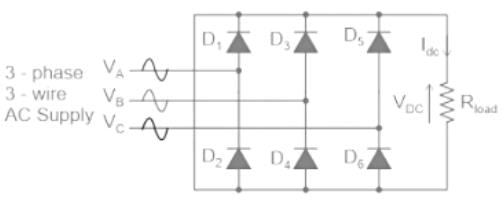
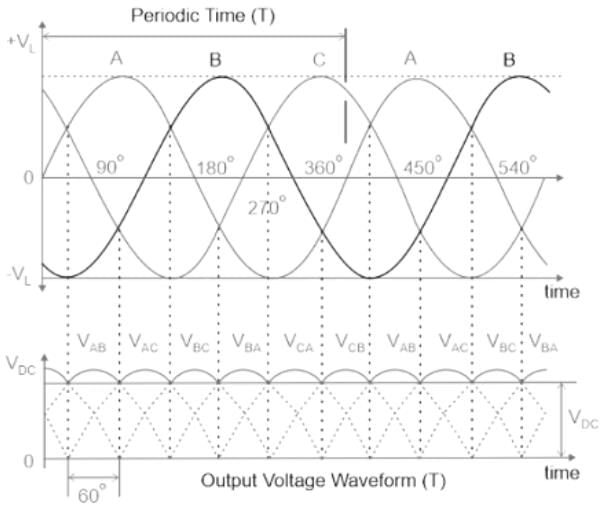
Average output voltage of a three-phase full wave diode rectifier is given by:
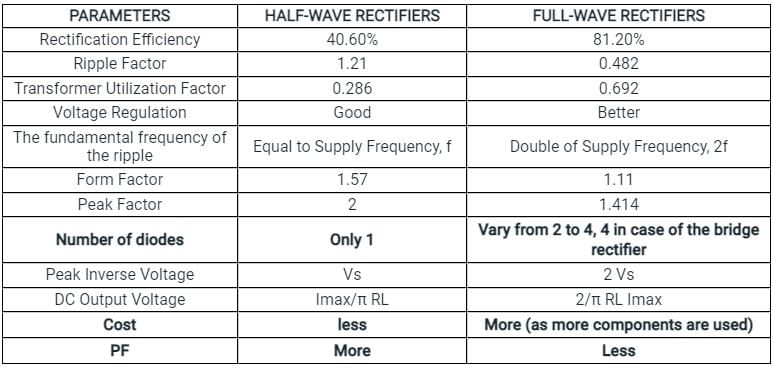
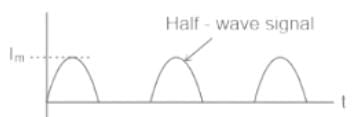
Calculate the rectification efficiency of half wave rectifier if input power to rectifier is 150 W and power obtained is 90 W.
The transformer Utilization factor of a bridge rectifier is approximately:
A single-phase full wave bridge diode rectifier delivers a constant current of 10 A to the load. Average and RMS values of source current are
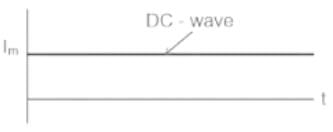
In the process of diode based rectification, the alternating input voltage is converted into