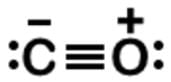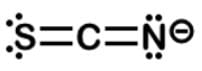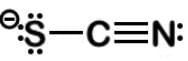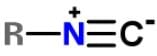Test: Dot Structures - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Dot Structures
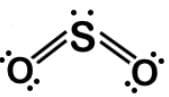
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a potent competitive inhibitor of hemoglobin, and it has an affinity for hemoglobin over 200 times greater than oxygen. What is the formal charge of the oxygen on the molecule?
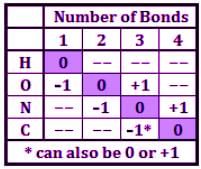
Thiocyanate is a potent competitive inhibitor of the thyroid sodium-iodide symporter and should be avoided by individuals suffering from hypothyroidism. What is the formal charge of the sulfur in the thiocyanate ion SCN−?
I. -2
II. -1
III. 0
IV. +1
II. -1
III. 0
IV. +1
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the difference between assigning formal charge and oxidation state?
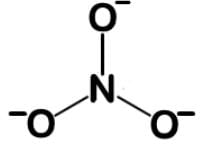
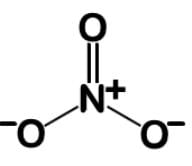
Nitrates are used to treat angina pectoris and acts to dilate the blood vessels to lower blood pressure. They exert their effects by their conversion into nitric oxide, a powerful vasodilator. What is the bond order and fractional charge on each oxygen of the nitrate ion?
Xanthocillin is a natural product extracted from the mold Penicillium notatum that has been used as an antibiotic and also contains the functional group isonitrile RNC. Which of the following resonance structures can be found for the functional group?
Which of the following compounds does NOT have a bent molecular geometry?
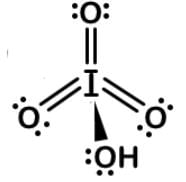
Periodic acid (H5IO6) will selectively cleave vicinal diols into two aldehyde or ketone fragments, which can be used to label the 3’-termini of RNA instead of DNA. Periodic acid can be dehydrated twice to form metal periodic acid. What are the molecular geometries of the two compounds respectively?
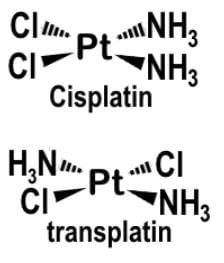
Cis-platin [PtCl2(NH3)2] is an anti-cancer drug that reacts by binding to and causing the crosslinking of DNA ultimately leading to apoptosis and is the geometric isomer of trans-platin. Given that cis-platin exhibits stereochemistry, what would you predict is the molecular geometry of the anticancer drug?
Determining Lewis dot structures can be used to determine whether a compound has any bond dipoles and consequently any molecular dipole. Which of the following compounds does NOT have a molecular dipole?
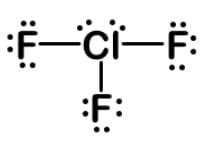
One method for sterilizing the surface of an article contaminated with bacteria and bacteria spores is using an interhalogen compound such as ClF3 or ClF5. What is the molecular geometry of chlorine trifluoride?