Test: Earthen Dams Failure - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Earthen Dams Failure
Provision of sufficient freeboard eliminates _____
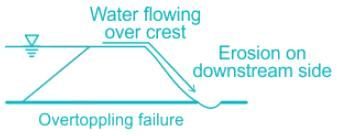
i. Over-topping failure
ii. Erosion of U/s face
iii. Erosion of D/s face
iv. Cracking due to frost action
v. Gully formation
Which of the following is/are correct?
i. Over-topping failure
ii. Erosion of U/s face
iii. Erosion of D/s face
iv. Cracking due to frost action
v. Gully formation
Which of the following is/are correct?
Stone pitching or riprap is generally provided to avoid _____
In order to prevent the possibility of the cross-flow towards the earthen embankments, it is necessary to provide _________
The collection and removal of water before it acquires high downward velocities is ensured by provision of ________
When the reservoir is full, the slope which is most likely to slide is _______
What is the most critical condition of slide of the U/s slope?
P% of earth dam failures are due to hydraulic failures, Q% of the earth dam failures are due to seepage failures, R% of the earth dam failures are due to structural failures, where
In order to keep the saturation line in a canal embankment well within the toe, it is necessary to provide _________