Test: Economy - 3 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Economy - 3
Which of the following statements is/ are correct about the Fiscal Responsibility Management Act (FRBMA), 2003?
1. States need to take prior permission from the central government for market borrowing.
2. It aimed to reduce Fiscal deficit and revenue deficit contingent liabilities and total liabilities.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
1. States need to take prior permission from the central government for market borrowing.
2. It aimed to reduce Fiscal deficit and revenue deficit contingent liabilities and total liabilities.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following statements does not correctly differentiate between Money market and Capital market?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If RBI cuts down the repo rate, it will have the following impact:
1. It may benefit the borrowers as EMIs (equated monthly instalments) will decrease.
2. It will increase investment in the economy.
3. It may lead to inflation in the country.
Which of the above statements are correct?
1. It may benefit the borrowers as EMIs (equated monthly instalments) will decrease.
2. It will increase investment in the economy.
3. It may lead to inflation in the country.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements about the MUDRA Bank:
1. It lends directly to the small and micro enterprises.
2. It is a differential bank.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements with respect to taxation of local governments in India:
1. Property taxes are the only sources of direct tax revenue at the third tier of government.
2. The tax collections of local governments from potentially buoyant sources of revenue are generally stacked at very low levels.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
The year 2019 marks the 50th anniversary of bank nationalization, the biggest structural reform introduced in the financial sector during the post-Independence period. In this context, consider the following objectives of nationalization:
1. To break the nexus between the banks and the big businesses that were disproportionately cornering bank finance for their narrow, selfish ends.
2. To ensure the balanced flow of credit to all the productive sectors, across various regions and social groups of the country.
3. To provide stability to the banking system by preventing bank failures and speculative activities.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Hybrid Annuity Model for infrastructure projects:
1. It is a mix of EPC (Engineering, Procurement and Construction) and BOT-Annuity (Buil-Operate-Transfer) Model.
2. Under it, the private player is responsible to construct and hand over the roads to the government who will in return collect the toll.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
The main objective of a payment bank is to further financial inclusion by providing small savings accounts and payments/remittance services to migrant labor workforce, lowincome households, small businesses, and other unorganized sector entities. In this context consider the following statements about the payment banks:
1. It is an example of universal banks in India.
2. It cannot undertake lending activities.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
With reference to Economic Census, consider the following statements:
1. In 2019 for the first time in the history of Independent India economic census was conducted.
2. It has been the means of measuring the diversity of non-farm economic activities.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Considers the following features of the new Rs. 200 denomination banknotes:
1. The note has motif of ‘Sanchi Stupa’ on it.
2. It bear signature of the Governor of Reserve Bank of India
3. Numerals in Devnagari.
4. Logo of Swachh Bharat.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Which of the following statements is/are correct about Digital India Programme?
1. High-speed internet as a core utility shall be made to the citizens in urban and semi-urban areas only.
2. Shareable private space on a public cloud.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements about the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF):
1. Only scheduled commercial banks can borrow from Reserve Bank of India under this window.
2. Banks can borrow funds only upto 1% of their net demand and time liabilities (NDTL).
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding Make in India Programme?
1. It promotes manufacturing sector only.
2. It is being led by Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
3. New Infrastructure is one of the core pillars of this programme.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Consider the following pairs of Committees and their recommendations:
1. Set Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC’s) for non-performing assets- N. Narasimham
2. Financial Inclusion and Technology Fund- C. Rangarajan
3. Regulatory and supervisory measures to address risk factor in NBFCs- Usha Thorat
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
Which of the following land reform measure(s) was/were taken by the government in postindependence period?
Consider the following statements regarding recent mergers of Public Sector Banks:
1. Merger of Punjab National Bank with Oriental Bank of Commerce and United bank of India will make it the largest lender in the country.
2. Merger of banks will provide benefits of economies of scale.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
With reference to UDAN Scheme, consider the following statements:
1. It’s a market-based model to develop regional connectivity.
2. It has a provision for Viability Gap Funding (VGF).
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which among the following is/are considered as the asset of Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
1. Loan given to the banks.
2. Bankers deposit to RBI.
3. Government Securities.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
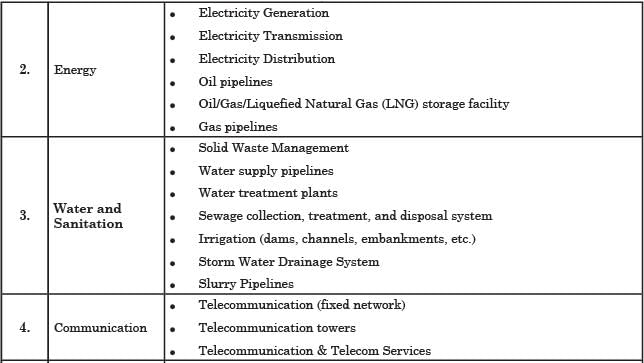
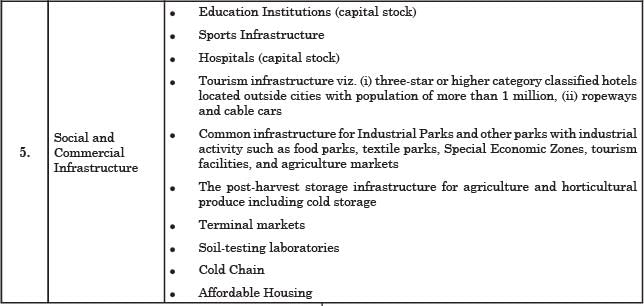
Which of the following sectors has/have been accorded the ‘infrastructure’ status in India?
Consider the following statements regarding the tools of monetary policy used by RBI:
1. Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) helps the RBI to transmit interest rate signals to the market.
2. In Open market Operations, central bank purchases or sells bonds in the open market in order to regulate money supply in the economy.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Consider the following statements about the Micro ATMs:
1. These are card swipe machines through which banks can remotely connect to their core banking system.
2. It has connectivity through Global System for Mobile (GSM) communication; hence it can travel from village to village.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding FDI in India:
1. The entry of FDI by non-resident citizens is regulated only through automatic route.
2. Government of India has provided 100% FDI under automatic route in single brand retailing.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
To strengthen banks and foster a culture of clean and responsible banking, the Government has followed a comprehensive 4 R’s approach. Which of the following comprises the 4R’s?
1. Resolution
2. Recapitalization
3. Reform
4. Restructuring
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements regarding Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana:
1. There is a uniform premium to be paid by farmers for all the crops.
2. There is no upper limit on Government subsidy.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about the Reserve Bank of India:
1. It was established in 1935, in accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
2. It manages the Foreign Exchange under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
3. It only Issues and exchanges currency and coins for circulation and have no power to destroy currency and coins.
Which of the above statements are correct?
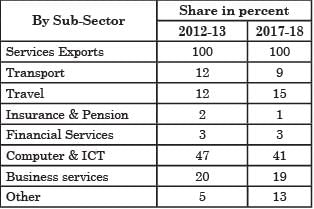
Consider the following statements regarding Service Sector in India:
1. The services sector accounts for more than 50 per cent of India’s Gross Value Added (GVA).
2. In total service export, transport sector has highest share.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Banks Board Bureau (BBB) is an autonomous body of the Government of India tasked to improve the governance of Public Sector Banks. In this context, consider the following statements:
1. It was set up under the government’s Indradanush program to reform public sector banks.
2. It recommends the selection of chiefs of government-owned banks and financial institutions and to help banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following is/are correct about National Anti-Profiteering Authority (NAA)?
1. It has been constituted under Income Tax Act.
2. It ensures that the reduction in the rate of tax is passed to the recipients.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Match the following pairs of Mint/Printing press with their locations:
1. India Government Mint - Nasik Road
2. India Security Press - Dewas
3. Bank Notes Press - Hyderabad
4. Bhartiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited - Mysore
Which of the above pairs is/are incorrectly matched?