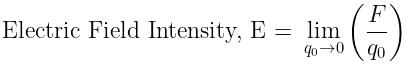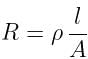Test: Electricity - 3 - Delhi Police Constable MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electricity - 3
The space around a charge in which its effect can be felt is called its
The force acting on a unit positive test charge at a point inside an electric field is called
Work done in moving a unit positive test charge from infinity to a point inside an electric field, is called
Work done is moving a unit positive test charge from one point to other inside an electric field, is called
Electricity constituted by electric charges at rest on the surface of a conductor, is called
Electricity constituted by moving electric charges, is called
Time rate of flow of electric charge measures electric _________.
The condition for an electric charge to flow from one point to other is that the two points must have electric
The device that maintains electric potential difference between two points is called electric
The path connecting two points at different potentials, to make the electric charges flow, is called electric _________.
The device which measures electric potential difference between two points is called
The device which measures electric current through a conductor is called
The law which gives a relation between electric potential difference and electric current is called
In series combination, resistance increases due to increase in
In parallel combination, resistance decreases due to increase in
Electrical resistivity of any given metallic wire depends upon
Substances whose atoms have more free electrons, are called