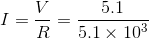CUET Exam > CUET Tests > Practice Tests for CUET UG Preparation > Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - CUET MCQ
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - CUET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Practice Tests for CUET UG Preparation - Test: Electronic Devices - 2
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 for CUET 2025 is part of Practice Tests for CUET UG Preparation preparation. The Test: Electronic Devices - 2 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the CUET exam syllabus.The Test: Electronic Devices - 2 MCQs are made for CUET 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 below.
Solutions of Test: Electronic Devices - 2 questions in English are available as part of our Practice Tests for CUET UG Preparation for CUET & Test: Electronic Devices - 2 solutions in
Hindi for Practice Tests for CUET UG Preparation course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for CUET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Electronic Devices - 2 | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for CUET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Practice Tests for CUET UG Preparation for CUET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 2
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 3
Which of the following properties does not characterise a semiconductor?
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 5
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 6
NAND and NOR gates are called universal gates primarily because they
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 6
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 7
A p-n junction diode is connected to a battery of emf 5.5 V and external resistance of 5.1 k. The barrier potential in the diode is 0.4 V. The current in the circuit is
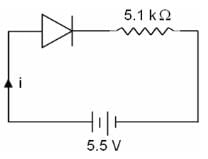
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 7
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 8
What is the output Y in the following circuit, when all the three inputs A, B and C are first 0 and then 1?

Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 8
Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 9
A full-wave rectifier is fed with AC mains of frequency 50 Hz. What is the fundamental frequency of ripple in the output current?
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 - Question 10
|
24 docs|1403 tests
|
Information about Test: Electronic Devices - 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Electronic Devices - 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Electronic Devices - 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice