Test: Electronic Devices & Circuits - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electronic Devices & Circuits - 1
At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to
Work function is the maximum energy required by the fastest electron at 0 K to escape from the metal surface.
The most commonly used semiconductor material is
In which of these is reverse recovery time nearly zero?
A transistor has a current gain of 0.99 in the CB mode. Its current gain in the CC mode is
In p-n-p transistor the current IE has two components viz. IEP due to injection of holes from p-region to n-region and IE due to injection of electrons from n-region to p-region. Then
The amount of photoelectric emission current depends on
In the circuit of figure the function of resistor R and diode D are 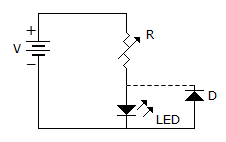
Assertion (A): A p-n junction has high resistance in reverse direction.
Reason (R): When a reverse bias is applied to p-n junction, the width of depletion layer increases.
At very high temperatures the extrinsic semi conductors become intrinsic because
When a voltage is applied to a semiconductor crystal then the free electrons will flow.
In a p type material the Fermi level is 0.3 eV above valence band. The concentration of acceptor atoms is increased. The new position of Fermi level is likely to be
In an n-p-n transistor, the majority carriers in the base are
An LED has a rating of 2 V and 10 mA. It is used along with 6V battery. The range of series resistance is
The number of doped regions in PIN diode is
A transistor has two p-n junctions. The batteries should be connected in active region such that
A silicon (PN) junction at a temperature of 20ºC has a reverse saturation current of 10 pico Ampere. The reverse saturation current at 40ºC for the same bias is approximately.
In a bipolar transistor the barrier potential
Recombination produces new electron-hole pairs
An amplifier without feedback has a voltage gain of 50, input resistance of 1 kΩ and output resistance of 2.5 kΩ. The input resistance of the current shunt -ve feedback amplifier using the above amplifier with a feedback factor of 0.2 is
As compared to an ordinary semiconductor diode, a Schottky diode
Assertion (A): When a high reverse voltage is applied to a p-n junction the diode breaks down.
Reason (R): High reverse voltage causes Avalanche effect.
As compared to an ordinary semiconductor diode, a Schottky diode



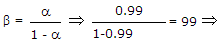 Current gain = 1 + β = 100.
Current gain = 1 + β = 100.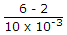 = 400Ω.
= 400Ω.
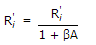 .
.
















