Test: Embryonic Development - CUET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Embryonic Development
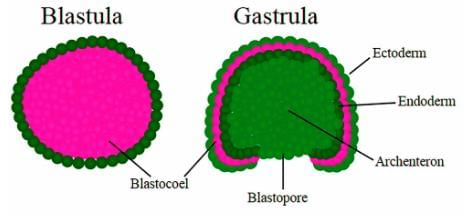
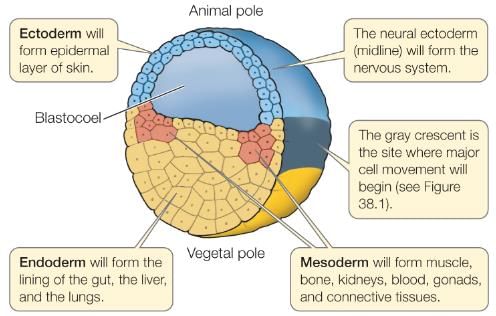
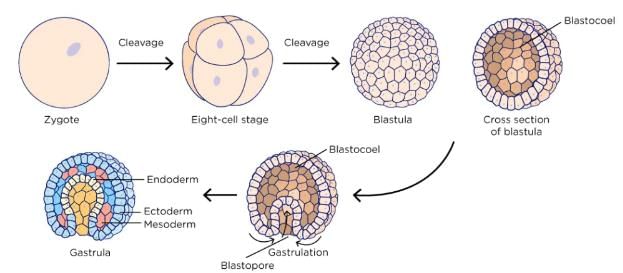
Three germ layers are formed during which stage of Embryonic development.
Movement of blastomeres usually seen in which Embryonic stage :-
The first movements of the foetus and appearance of hair on the head are usually observed during the :-
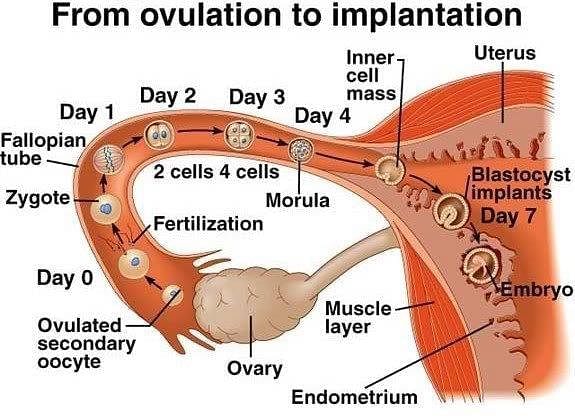
Solid ball of cell produced by repeated cleavage is called
The first indication of division of labour in the blastomeres appear at
Sexually reproducing multicellular animals start their development from -
Preparation of cell differentiation are completed in-
A scientist was looking at using different hormones in the blood as a marker for pregnancy. Which of the following hormones will not be ideal for this?
The first sign of growing foetus may be noticed by :-
During pregnancy only which hormones are secreted in women :-
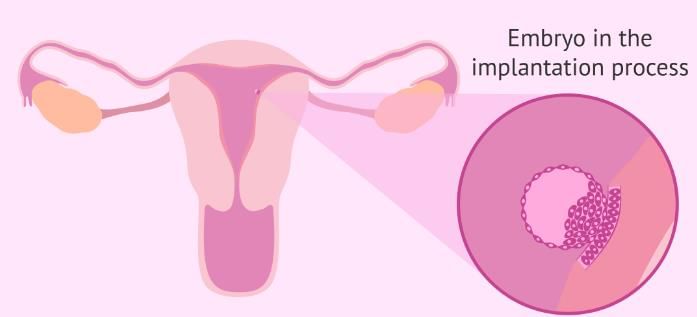
During Implantation, the blastocyst becomes embedded in the which layer of the uterus.
Name the embryonic stage that gets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.