Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Tests > Test: Equivalent Resistance - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Equivalent Resistance
Test: Equivalent Resistance for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Test: Equivalent Resistance questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus.The Test: Equivalent Resistance MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Equivalent Resistance below.
Solutions of Test: Equivalent Resistance questions in English are available as part of our course for Electrical Engineering (EE) & Test: Equivalent Resistance solutions in
Hindi for Electrical Engineering (EE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Equivalent Resistance | 10 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 1
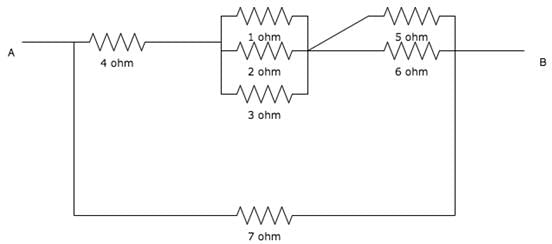
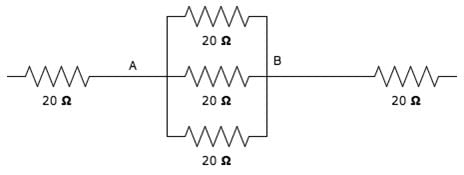
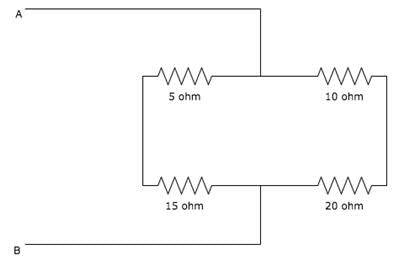
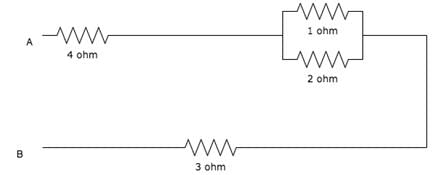
Calculate the total resistance between the points A and B.

Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 4
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 5
It is preferable to connect bulbs in series or in parallel?
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 6
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 7
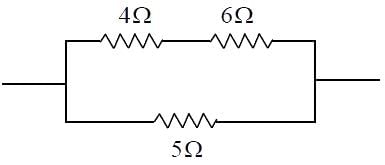
In the circuit shown in figure, the heat produced in the 5 Ω resistor due to the current flowing through it is 10 cal s-1. The heat generated in the 4 Ω resistor is
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 8
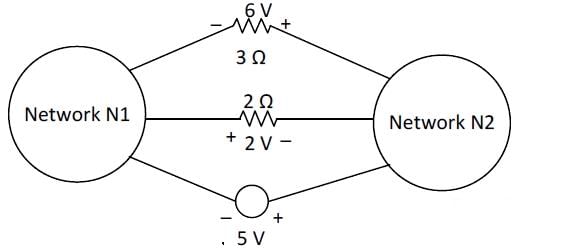
The voltages developed across the 3Ω and 2Ω resistors shown in the figure are 6V and 2V respectively, with the polarity as marked. What is the power (in Watt) delivered by the 5V voltage source?
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 8
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 9
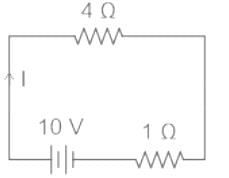
The terminal voltage of the battery, whose emf is 10 V and internal resistance 1 Ω, when connected through an external resistance of 4 Ω as shown in the figure is:
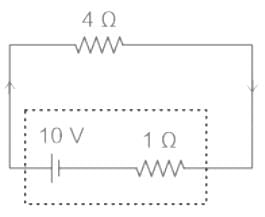
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 9
Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 10
Select the correct dual pair of voltage source, current source, inductor and capacitor.
Detailed Solution for Test: Equivalent Resistance - Question 10
Information about Test: Equivalent Resistance Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Equivalent Resistance solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Equivalent Resistance, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF