Test: Estimation and Costing- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Civil Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Test: Estimation and Costing- 1
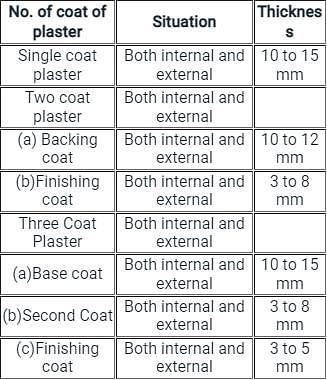
Unless otherwise specified, thickness of plaster should be kept
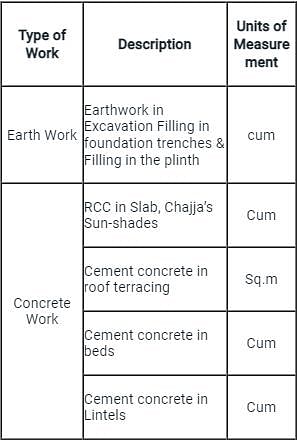
The unit of measurement for earthwork in surface excavation exceeding 1.5 m in width as well as 10 sqm on plan but not exceeding 30 cm in depth, is in :
A room is 4 m × 3 m with 20 cm walls all around. The estimate of walls by central line method will be
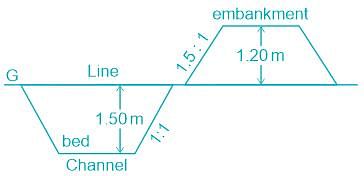
What is the lift of soil material for the canal shown in the figure?

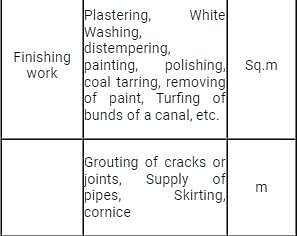
Unit of measurement for roofing tiles is specified in terms of
To make ten cubic metre of 1 ∶ 2 ∶ 4 by volume concrete, the volume of coarse aggregates required is
What is the quantity of cement (in kg) and of dry sand (in cubic meter) respectively required for preparing 1 cubic meter of wet cement mortar of 1 : 5 proportion?
The carpet area of a residential building is generally _______ of its plinth area.
In which type of estimate is 'Court yard' NOT considered?
|
2 videos|122 docs|55 tests
|