Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: First Law of Thermodynamics - 2
The inlet and the outlet conditions of steam for an adiabatic steam turbine are as indicated in the figure. The notations are as usually followed.
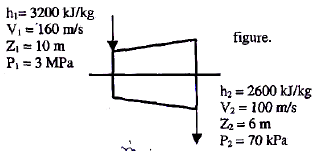
Assume the above turbine to be part of a simple Rankine cycle. The density of water at the inlet to the pump is 1000 kg/m3. Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, the specific work (in kJ/kg) supplied to the pump is:
A gas contained in a cylinder is compressed, the work required for compression being 5000 kJ. During the process, heat interaction of 2000 kJ causes the surroundings to the heated. The change in internal energy of the gas during the process is:
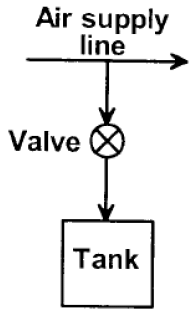
A rigid, insulated tank is initially evacuated. The tank is connected with a supply line through which air (assumed to be ideal gas with constant specific heats) passes at I MPa, 350°C. A valve connected with the supply line is opened and the tank is charged with air until the final pressure inside the tank reaches I MPa. The final temperature inside the tank
In an adiabatic process, 5000J of work is performed on a system. The system returns to its original state while 1000J of heat is added. The work done during the non-adiabatic process is:
Given that the path 1-2-3, a system absorbs 100kJ as heat and does 60kJ work while along the path 1-4-3 it does 20kJ work (see figure given). The heat absorbed during the cycle 1-4-3 is:
The efficiency of a reversible cyclic process undergone by a substance as shown in the given diagram is:
The heat transferred in a thermodynamic cycle of a system consisting of four processes is successively 0, 8, 6 and -4 units. The net change in the internal energy of the system will be:
In an adiabatic process 6000 J of work is performed on a system. In the nonadiabatic process by which the system returns to its original state 1000J of heat is added to the system. What is the work done during non-adiabatic process?
In a test of a water-jacketed compressor, the shaft work required is 90 kN-m/kg of air compressed. During compression, increase in enthalpy of air is 30 kJ/kg of air and increase in enthalpy of circulating cooling water is 40 kJ/ kg of air. The change is velocity is negligible. The amount of heat lost to the atmosphere from the compressor per kg of air is:
A gas chamber is divided into two parts by means of a partition wall. On one side, nitrogen gas at 2 bar pressure and 20°C is present. On the other side, nitrogen gas at 3.5 bar pressure and 35°C is present. The chamber is rigid and thermally insulated from the surroundings. Now, if the partition is removed,
Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
An ideal cycle is shown in the figure. Its thermal efficiency is given by
A closed system undergoes a process 1-2 for which the values of Q1-2 and W1-2 are +20 kJ and +50 kJ, respectively. If the system is returned to state, 1, and Q2-1 is -10 kJ, what is the value of the work W2-1?
In a steady-flow adiabatic turbine, the changes in the internal energy, enthalpy, kinetic energy and potential energy of the working fluid, from inlet to exit, are -100 kJ/kg, -140 kJ/kg, -10 kJ/kg and 0 kJ/kg respectively. Which one of the following gives the amount of work developed by the turbine?
A system while undergoing a cycle
A – B – C – D – A has the values of heat and work transfers as given in the Table:
The power developed in kW is, nearly,
A tank containing air is stirred by a paddle wheel. The work input to the paddle wheel is 9000 kJ and the heat transferred to the surroundings from the tank is 3000 kJ. The external work done by the system is:
Assertion (A): The internal energy depends on the internal state of a body, as determined by its temperature, pressure and composition.
Reason (R): Internal energy of a substance does not include any energy that it may possess as a result of its macroscopic position or movement.
170 kJ of heat is supplied to a system at constant volume. Then the system rejects 180 kJ of heat at constant pressure and 40 kJ of work is done on it. The system is finally brought to its original state by adiabatic process. If the initial value of internal energy is 100 kJ, then which one of the following statements is correct?
A closed system receives 60 kJ heat but its internal energy decreases by 30 kJ. Then the work done by the system is
A system undergoes a process during which the heat transfer to the system per degree increase in temperature is given by the equation:
dQ/dT = 2 kJ/°C The work done by the system per degree increase in temperature is given by the equation dW/dT = 2 – 0.1 T, where T is in °C. If during the process, the temperature of water varies from 100°C to 150°C, what will be the change in internal energy?
Consider the following statements:
1. The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy.
2. Perpetual motion machine of the first kind converts energy into equivalent work.
3. A closed system does not exchange work or energy with its surroundings.
4. The second law of thermodynamics stipulates the law of conservation of energy and entropy.
Which of the statements are correct?
For steady flow through an insulated horizontal constant diameter pipe, this property remains constant
A 4 kW, 20 litre water heater is switched on for 10 minutes. The heat capacity Cp for water is 4 kJ/kg K. Assuming all the electrical energy has gone into heating the water, what is the increase of the water temperature?
A reversible heat engine operating between hot and cold reservoirs delivers a work output of 54 kJ while it rejects a heat of 66 kJ. The efficiency of this engine is:
Match List-I (Devices) with List-II (Thermodynamic equations) and select the correct answer using the codes below the lists:



















