NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Tests > Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - NEET PG MCQ
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - NEET PG MCQ
Test Description
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Pharmacology - 2
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 for NEET PG 2025 is part of NEET PG preparation. The Test: General Pharmacology - 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the NEET PG exam syllabus.The Test: General Pharmacology - 2 MCQs are made for NEET PG 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 below.
Solutions of Test: General Pharmacology - 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for NEET PG & Test: General Pharmacology - 2 solutions in
Hindi for NEET PG course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET PG Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: General Pharmacology - 2 | 25 questions in 25 minutes | Mock test for NEET PG preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for NEET PG Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 1
Volume of distribution of drugs is altered in: (PGI June, 2004)
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 1
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 2
Which of the following are prodrugs? (PGI Dec. 2004)
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 2
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 3
High first pass metabolism is seen in: (PGI Dec. 2004)
*Multiple options can be correct
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 5
High hepatic extraction ratio is seen in: (PGI June, 2002)
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 6
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 7
The process by which the amount of a drug in the body decreases after administration but before entering the systemic circulation is called:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 7
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 8
The most general term for the process by which the amount of active drug in the body is reduced after absorption into the systemic circulation is:
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 9
Titration of the dose of a drug with the response can be done with which of the following routes of administration:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 9
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 10
Urinary alkalinizing agents are administered in case of poisoning due to drugs which are:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 10
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 11
Which of the following drugs has maximum chances of absorption from gastric mucosa?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 11
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 12
All of the following factors tend to increase the volume of distribution of a drug EXCEPT:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 12
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 13
Which of the following drugs is commonly administered by intranasal route?
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 14
Maj or mechanism of transport of drugs across biological membranes is by:
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 15
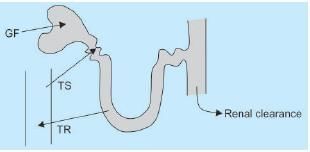
A drug X is secreted through renal tubules, tubular secretion of this drug can be confirmed if renal clearance of drugX is:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 16
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 17
A new drug is found to be highly lipid soluble. It is metabolized at a slower rate of 10% per hour. On intravenous injection it produces general anaesthesia that lasts only for 15 min. This short duration of anaesthesia is due to:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 17
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 18
All of the following are advantages of transdermal drug delivery systems EXCEPT:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 18
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 19
Thiopentone is used for induction of anaesthesia. It shows marked redistribution which is a characteristic of:
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 21
Which of the following statements about a drug having high plasma protein binding is TRUE?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 21
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 22
Most common phase II drug metabolizing reaction is:
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 23
All of the following reactions are catalyzed by microsomal enzymes EXCEPT:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 23
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 24
Which of the following factors has maximum effect on filtration of a drug by the glomerulus?
Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 25
A factor that is likely to increase the duration of action of a drug D that is partially metabolized by CYP3A4 in the liver is:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 - Question 25
Information about Test: General Pharmacology - 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: General Pharmacology - 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: General Pharmacology - 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF