Test: Geography- 6 - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Geography- 6
Consider the following statements
- Black soils are rich in Iron, magnesia and alumina.
- Laterite soils are rich in lime, iron oxide and aluminium compounds.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
- The soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall.
- They are generally poor in nitrogen, phosphorous and humus.
- They are fertile when fine-grained and are poor in fertility when they are coarse-grained.
The above statements refer to:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following are not the tributaries of river Kaveri
- Kabini
- Bhima
- Amravati
- Koyna
- Manjra
Select the correct code:
Which of the following are the characteristics of Submergent coastlines
- Drowned river valleys
- Wave cut platform
- Presence of fjords
Select the correct code:
Which of the following lake is NOT part of Great Lakes region of North America
Which one of the following places is located at the confluence of Alaknanda and Bhagirathi
Consider the following statements regarding Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS).
- Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) is an intergovernmental organization of low- lying coastal and small island countries.
- The main purpose of the alliance is to consolidate the voices of Small Island Developing States (SIDS) to address global warming.
- AOSIS partners with United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to effectively influence climate negotiations.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following statement is correct regarding Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) initiative.
Consider the following statements about Asia-Pacific awards for cultural heritage conservation.
- It is awarded by UNESCO.
- It recognises the efforts taken to restore and conserve historical structures without affecting their heritage value.
- New Delhi has won most recognitions in India since the inception of the awards.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Carbon offsetting.
- Carbon offsetting allows a country to help reach its own emissions reduction targets by funding emission reductions in another country.
- The United Nations Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) set up under the 1997 Kyoto Protocol is first major Carbon offsetting scheme.
- Carbon offsets can be bought by individuals, companies or countries.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD).
- The western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer and then colder than the eastern part of the ocean.
- A study has demonstrated a significant correlation between the IOD and drought in the southern half of Australia.
- IOD can either aggravate or weaken the impact of El Nino on Indian monsoon.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
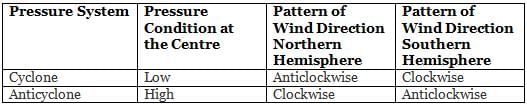
Consider the following statements about anticyclone?
- It is an area of high pressure.
- The wind direction is Anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
The most prominent feature in the oceans, forming an almost continuous mountain range, is the
Qatar is bordered by which of the following countries.
- United Arab Emirates
- Bahrain
- Saudi Arabia
Select the correct code:
The California Ocean current, which flows along the west coast of North America, is a
Which of the following port is known as “Queen of Arabian Sea”?
Which of the following factors affect Ocean Salinity?
- Evaporation
- Wind
- Influx of river water
- Ocean currents
- Precipitation
Select the correct code:
December and January are the coldest months in the northern plain. The reasons for the excessive cold in north India are:
- Far away from the sea.
- Snowfall in the nearby Himalayan ranges
- Cold winds coming from Taklamakan Desert and Plateau of Tibet.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
- ITCZ is also known as doldrums
- ITCZ is an area encircling the Earth near the Equator, where the northeast and southeast trade winds converge
- ITCZ has no effect on tropical cyclone formation
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following explains why one side of a mountain usually has more precipitation than the other side?