Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Tests > Mathematics Olympiad Class 4 > Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Class 4 MCQ
Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Class 4 MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics Olympiad Class 4 - Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4
Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 for Class 4 2025 is part of Mathematics Olympiad Class 4 preparation. The Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Class 4 exam syllabus.The Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 MCQs are made for Class 4 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 below.
Solutions of Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 questions in English are available as part of our Mathematics Olympiad Class 4 for Class 4 & Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 solutions in
Hindi for Mathematics Olympiad Class 4 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Class 4 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for Class 4 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Mathematics Olympiad Class 4 for Class 4 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 4
Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 5
Mr. Khanna is traveling with ₹ 20000. Using the clues given below, find the amount left with him when he reaches his destination.
Clues: (a) He fills up petrol for ₹ 3200.
(b) He buys a meal for ₹ 4850.
(c) He buys souvenirs for ₹ 2100.
(d) He spends ₹ 1350 on snacks.
(e) He gives ₹ 500 each to three helpers after reaching his destination.
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 7
Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 8
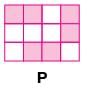
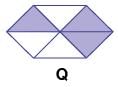
Study the given figures carefully and select the INCORRECT option based on the figures.
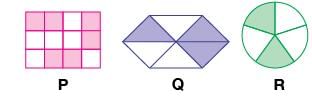
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 8
Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 9
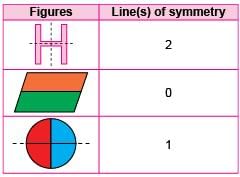
Match the figures given in Column I with their number of line(s) of symmetry given in Column II and select the CORRECT option.
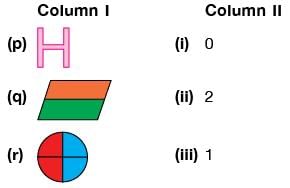
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 9
Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 10
Identify the 4-digit number using given clues.
- The sum of all of its digits is 20.
- The digit at ones place is the HCF of 4 and 12.
- The digit at hundreds place is the second multiple of the digit at ones place.
- The digit at thousands place is the greatest 1-digit prime number.
Detailed Solution for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 - Question 10
|
32 videos|39 docs|46 tests
|
Information about Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: High Order Thinking Skills - 4, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice