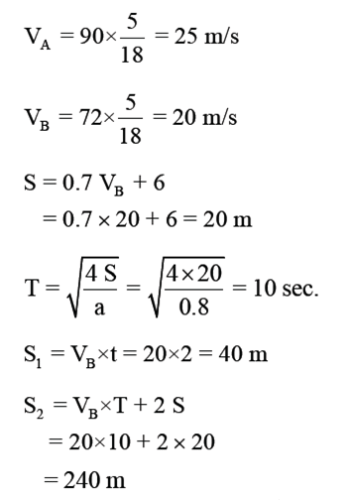Test: Highway - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Highway
The speed of overtaking and overtaken vehicles are 90 Kmph and 72 Kmph respectively. Calculate the overtaking sight distance. Assume acceleration of overtaking vehicle as 0.8 m/s2 and traffic stream moves in one way.
A car moves at a speed of 90 Kmph on a road having 5% downward gradient. If the reaction time of the driver is 2 seconds, assuming that f = 0.15, calculate the distance moved by the vehicle before the car stops finally after the brakes are applied ? Take g = 10 m/s2
A roundabout is provided with an average entry width of 8.4 m, width of weaving section as 14 m, and length of the weaving section between channelizing islands as 35 m. The crossing traffic and total traffic on the weaving section are 1000 and 2000 PCU per hour respectively. The nearest rounded capacity of the roundabout (in PCU per hour) is
The traffic count on road is proposed to be 2500 commercial vehicles per day. Growth of traffic is 5 percent vehicle damage factor = 2.5. The design Life of pavement is 10 years and traffic distribution factor can be adopted as 0.5. What are the cumulative standard axles (MSA)?
If the modulus of sub-grade reaction of standard plate of 30 cm diameter is 20 Kg/cm3, the value for a standard plate of 75cm diameter is:
The bitumen content in the Marshal specimen of bitumenous concrete is 5% of the total weight of the mix.
The theoretical and measured unit weights of the mix are 2.5 g/cm3 and 2.4 g/cm3 respectively. The bitumen has specific gravity of 1. The percentage voids in mineral aggregates filled with bitumen (VFB) are:
The consistency and flow resistance of bitumen can be determined from which of the following?
The following observations were made of an axle-load survey on a road:
The standard axle Load is 80kN. Equivalent daily number of repetitions for the standard axle Load are:
Radius of relative stiffness of cement concrete pavement does not depend upon which one of the following?
What will be the ruling radius of a horizontal curve on a national highway for a design vehicle speed of 100 Km/h assuming allowable super elevation to be 7% and Lateral friction as 0.13?
For a given road, safe stopping sight distance is 80m and passing sight distance is 300m. What is the intermediate sight distance?
A summit curve is formed at the intersection of a 3% upgrade and a 5% downgrade. What is the length of the summit curve in order to provide a stopping distance of 128m?
On a road the free speed was 65 Kmph and the space headway at jam density was 6.25m. What is the maximum flow which should be expected on this road?
In spot speed study, which one is considered the design speed on highway?
In floating car method, following observations are made when floating car moves in N-S direction
No. of Vehicles overtaken by the test vehicle = 155
No. of vehicles overtaking the test vehicle = 105
Vehicles counted in S-N direction when test vehicle moves in N-S direction =80
Vehicles counted in N-S direction when test vehicle moves in N-S direction = 75
Length of road stretch = 0.5 Km
Speed of test vehicle = 20 Kmph
Calculate the average journey time of the traffic stream in N-S direction?
A district road with a bituminous pavement has a horizontal curve of 1000 m for a design speed of 75 km ph. The super-elevation is
A mixture contains coarse aggregates (GS = 2.7), fine aggregates (GS = 2.9), Mineral filler (GS = 1.5) in the proportion 50:40:10 (by weight). These materials are mixed with bitumen (GS = 1.2) and compacted, the unit
weight becomes 2300 Kg/m3 and contains 5% voids. Calculate the voids in mineral aggregates for the given specimen?
A two Lane urban road with one way traffic has a maximum capacity of 2000 vehicles/hour. Under the jam condition the average length occupied by the vehicles is 5m. The speed versus density relationship is
linear. For a traffic volume of 1200 vehicles per hour, the density (in vehicles/Km) is:
An observer counts 300 vehicles/hour at a specific highway location. Assume that the vehicle arrival at the Location is Poisson’s distribution, the probability of having one vehicle arriving over a 30 second time interval is.......
On a specific highway, the speed density relationship follows the Greenberg’s Model , where vf and KJ are the free flow speed and jam density respectively when the highway is operating at capacity, the density obtained as per this model is:
If the pressure carried by a CBR specimen at 2.5mm penetration is 3.5 N/mm2, the CBR of the soil is:
The width of expansion joint gap is 2.5cm, in a cement concrete pavement. If the minimum and maximum temperature of slab are 10oC and 30oC, calculate the spacing between expansion joints. Assume coefficient of thermal expansion of concrete is 10 × 10-6 per oC. Assume that joint filler can be compressed up to 50%.........m
(Important - Enter only the numerical value in the answer)
If the load, warping and frictional stresses in a cement concrete slab are 210 N/mm2, 290 N/mm2 and 10 N/mm2 respectively, the critical combination of stresses during summer mid-day is: