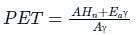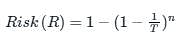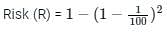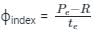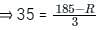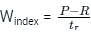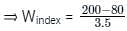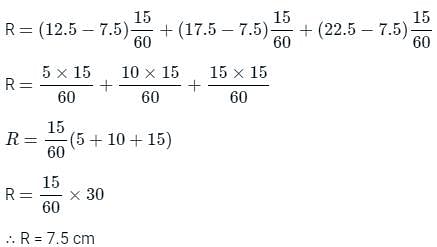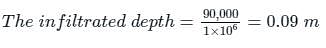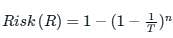Test: Hydrology - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Engineering Hydrology - Test: Hydrology
What is the process by which water enters the small pore spaces between particles in soil rock?
The hydrologic risk of a 100 year flood occuring during the 2-year service life of a project is
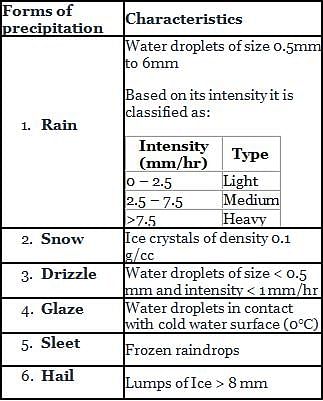
The rainfall figures for successive 30 – minute intervals are 35, 40, 120, 85, 45, 45 and 30 mm/hr. If the ϕ index is 35 mm/hour, determine W-index.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Isochrones are curves of equal pore water pressure
2. Isochrones depict the variation of the pore water pressure along with the depth of the soil sample
3. Isochrones vary with time
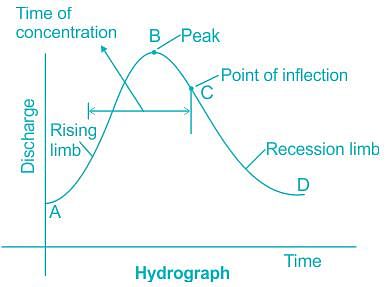
Select the correct option with regard to the following two statements (H1 and H2) pertaining to the hydrograph of a storm in a catchment.
H1: The rising limb of the hydrograph depends on the catchment characteristics only.
H2: The recession limb of the hydrograph depends on the storm characteristics and catchment characteristics.
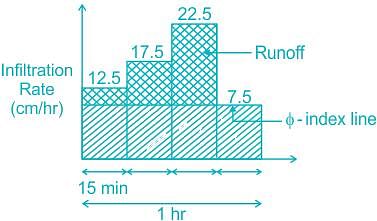
During a storm, the rates of rainfall observed at a frequency of 15 min for one hour are 12.5, 17.5, 22.5 abd 7.5 cm/h. If the phi-index is 7.5 cm/h, then the total run-off will be
Rainfall of intensity 20 mm/h occurred over a watershed of area 1 km2 for duration of six hours. It measures a direct runoff for a volume of 30,000 m3 in the stream. Find the precipitation NOT available for runoff in this case?
The total quantity of water on the surface of earth is estimated as about
A culvert is designed for a flood frequency of 100 years and a useful life of 20 years. The risk involved in the design of the culvert (in percentage up to two decimal places)
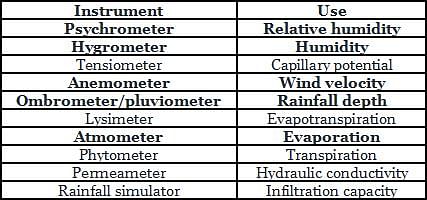
Which one of the following points should be kept in mind while selecting the site for a rain gauge station?
The observed annual runoff from a basin of area 500 km2 is 150 Mm3 and the corresponding annual rainfall over the basin during the same year is 750 mm. What is the runoff coefficient?
A canal is 80 km long and has an average surface width of 15 m. If the evaporation measured in a class A pan is 0.5 cm/day, the volume of water evaporated in a month of 30 days is (in m3)
|
20 videos|36 docs|30 tests
|