Test: Inflammation- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Inflammation- 1
After binding of complement and antibody on the surface of encapsulated bacteria, the process of phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes involves which of the following? (AIIMS Nov 2011)
Which among the following is the hallmark of acute inflammation? (AI 2011, AIIMS May 2010)
A 72 year-old man Kishori Lal presented to surgery OPD with a history of difficulty in micturition, increased frequency of urine and lower backache for the past 8 months. Digital rectal examination reveals an enlarged prostate with irregular surface. The surgeon orders for the serum PSA levels which are found to be increased and X ray spine shows osteoblastic lesions. A diagnosis of metastatic prostate cancer is made. Mr Lal also complaints of significant weight loss, loss of appetite and loss of energy over the past 45 days. His current complaints can be attributed to which of the following?
A 14-year-old girl Radha has high grade fever. She goes to a physician Dr. Jeeva Roy who orders for some blood investigations. A complete blood count with differential implies the presence of a viral infection. Which of the following best describes the cells that indicate a viral etiology to her illness?
Endothelium leukocyte interaction during inflammation is mediated by/due to (PGI, Dec 2003)
A 28-year-old woman, Vimla is being evaluated to find the cause of her urine turning a dark brown color after a recent upper respiratory tract infection. She has been otherwise symptomatic, and her blood pressure has been within normal limits. Urinalysis finds moderate blood present with red cells and red cell casts. Immunofluorescence examination of a renal biopsy reveals deposits of IgA within the mesangium. These clinical findings suggest that her disorder is associated with activation of the alternate complement system. Which of the following serum laboratory findings is the most suggestive of activation of the alternate complement system rather than the classic complement system?
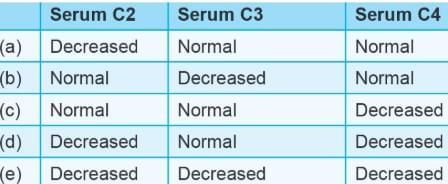
An 18-year-old woman, Sheila is being evaluated for recurrent facial edema, especially around her lips. She also has recurrent bouts of intense abdo-minal pain and cramps, sometimes associated with vomiting. Laboratory examination finds decreased C4, while levels of C3, decay-accelerating factor, and IgE are within normal limits. A deficiency of which one of the following substances is most likely to be associated with these clinical findings?
Interleukin secreted by macrophages, stimulating lymphocytes is:
In acute inflammation due to the contraction of endothelial cell cytoskeleton, which of the following results? (AIIMS Nov 2006)
Which of the following statements in context of the enzyme ‘E’ shown in the diagram given below is correct?
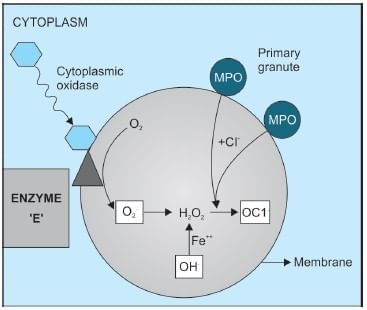
In genetic deficiency of MPO the increased susceptibility to infection is due to: (Delhi PG 09 RP)



















