Test : Introduction Of IVC And IVC Cities - UPSC MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test : Introduction Of IVC And IVC Cities
With reference to Indus Valley Civilization, consider the following statements:
1. It is also called Bronze age civilization
2. It flourished around 3500 BC.
3. The script of it is not deciphered.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. It is also called Bronze age civilization
2. It flourished around 3500 BC.
3. The script of it is not deciphered.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following sites is/are part of the Mature Harappan phase?
1. Mehrgarh
2. Harappa
3. Mohenjo-daro
4. Lothal
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
1. Mehrgarh
2. Harappa
3. Mohenjo-daro
4. Lothal
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Match the following pairs;
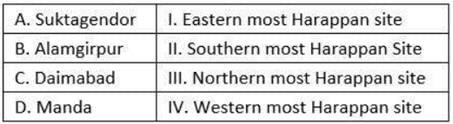
Select the correct answer using the code given below:

Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Arrange the following Indus Valley Sites in chronological order of their discovery:
1. Harappa
2. Chanhudaro
3. Mohenjodaro
4. Banwali
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Indus Valley Civilization belongs to which of the following period?
Lothal, a prominent site of Indus Valley Civilization, is situated in
Which of the following Harappan sites are not in India?
Who among the following referred to Indus Valley Civilization as the Harappan culture?
Which one of the following Harappan site does suggest ploughing (evidence of furrow) Identify it.
It is found in Mesopotamian records that there were two intermediate trading stations between Mesopotamia and Harappan regions. Identify the places.



















