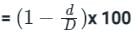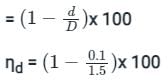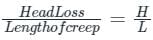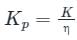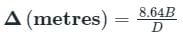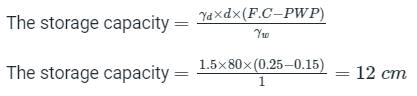Test: Irrigation Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Irrigation Engineering - Test: Irrigation Engineering
Determine its distribution efficiency when mean depth of water is 1.5 cm and the mean deviation from the mean is 0.1 cm.
In an assumption made in the Bligh's Creep Theory for design of impervious floor for sub surface flow, the hydraulic gradient
The element that worries about the proliferation of weeds is :
To design a cantilever type, the height of the retaining wall is ______?
The time taken between the sowing and harvesting of crops called
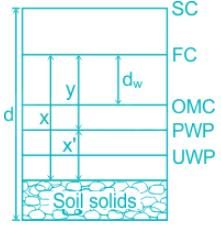
The field capacity of a soil is 25%, its permanent wilting point is 15% and specific dry unit weight is 1.5 g/cc. If the depth of the root zone of a crop is 80 cm, the storage capacity of the soil is
The minimum furrow grade to assure surface drainage is:
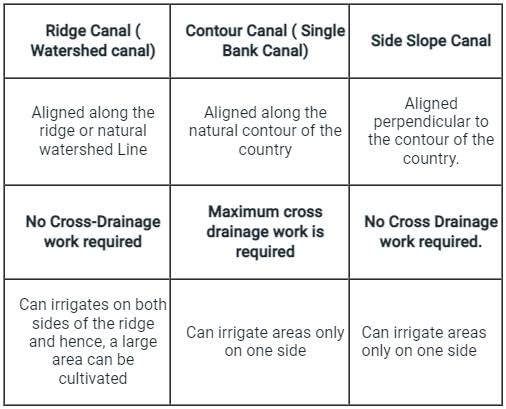
Among the classification of canals based on alignment criteria, identify the canal in which the number of cross drainage works is maximum?
|
7 videos|49 docs|31 tests
|