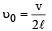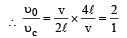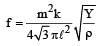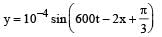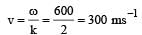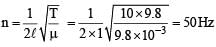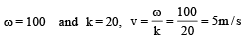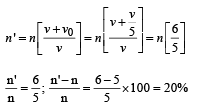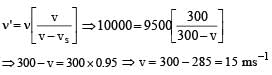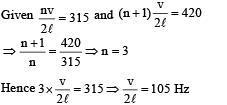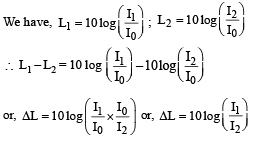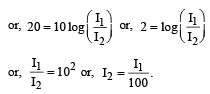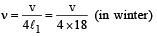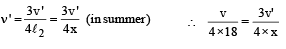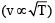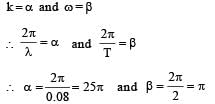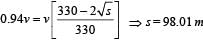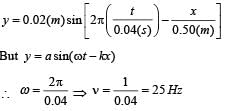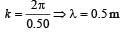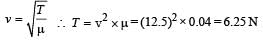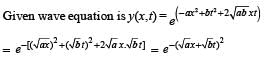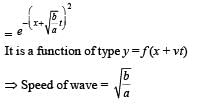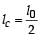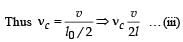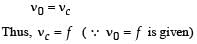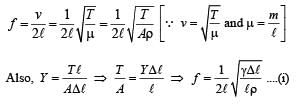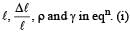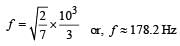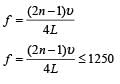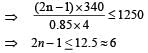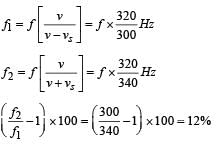Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Waves - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Waves
Waves y1 = A cos(0.5πx - 100πt) and y2 = A cos(0.46πx - 92πt) are travelling along x-axis. (Here x is in m and t is in second)
Q. Find the number of times intensity is maximum in time interval
Waves y1 = A cos(0.5πx - 100πt) and y2 = A cos(0.46πx - 92πt) are travelling along x-axis. (Here x is in m and t is in second)
Q. The wave velocity of louder sound is
Waves y1 = A cos(0.5πx - 100πt) and y2 = A cos(0.46πx - 92πt) are travelling along x-axis. (Here x is in m and t is in second)
Q. The number of times y1 + y2 = 0 at x = 0 in 1 sec is
Two trains A and B moving with speeds 20 m/s and 30 m/s respectively in the same direction on the same straight track, with B ahead of A. The engines are at the front ends. The engine of train A blows a long whistle.
Assume that the sound of the whistle is composed of components varying in frequency from f1 = 800 Hz to f2 = 1120 Hz, as shown in the figure. The spread in the frequency (highest frequency – lowest frequency) is thus 320 Hz. The speed of sound in still air is 340 m/s.
Q. The speed of sound of the whistle is
Two trains A and B moving with speeds 20 m/s and 30 m/s respectively in the same direction on the same straight track, with B ahead of A. The engines are at the front ends. The engine of train A blows a long whistle.
Assume that the sound of the whistle is composed of components varying in frequency from f1 = 800 Hz to f2 = 1120 Hz, as shown in the figure. The spread in the frequency (highest frequency – lowest frequency) is thus 320 Hz. The speed of sound in still air is 340 m/s.
Q. The distribution of the sound intensity of the whistle as observed by the passengers in train A is best represented by
Two trains A and B moving with speeds 20 m/s and 30 m/s respectively in the same direction on the same straight track, with B ahead of A. The engines are at the front ends. The engine of train A blows a long whistle.
Assume that the sound of the whistle is composed of components varying in frequency from f1 = 800 Hz to f2 = 1120 Hz, as shown in the figure. The spread in the frequency (highest frequency – lowest frequency) is thus 320 Hz. The speed of sound in still air is 340 m/s.
Q. The spread of frequency as observed by the passengers in train B is
Length of a string tied to two rigid supports is 40 cm. Maximum length (wavelength in cm) of a stationary wave produced on it is
Tube A has both ends open while tube B has one end closed, otherwise they are identical. The ratio of fundamental frequency of tube A and B is
A tuning fork arrangement (pair) produces 4 beats/sec with one fork of frequency 288 cps. A little wax is placed on the unknown fork and it then produces 2 beats/sec. The frequency of the unknown fork is
A wave y = a sin(ωt–kx) on a string meets with another wave producing a node at x = 0. Then the equation of the unknown wave is
When temperature increases, the frequency of a tuning fork
The displacement y of a wave travelling in the x -direction is given by 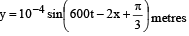 where x is expressed in metres and t in seconds. The speed of the wave - motion, in ms-1 , is
where x is expressed in metres and t in seconds. The speed of the wave - motion, in ms-1 , is
A metal wire of linear mass density of 9.8 g/m is stretched with a tension of 10 kg-wt between two rigid supports 1 metre apart. The wire passes at its middle point between the poles of a permanent magnet, and it vibrates in resonance when carrying an alternating current of frequency n. The frequency n of the alternating source is
A tuning fork of known frequency 256 Hz makes 5 beats per second with the vibrating string of a piano. The beat frequency decreases to 2 beats per second when the tension in the piano string is slightly increased. The frequency of the piano string before increasing the tension was
The displacement y of a particle in a medium can be expressed as, 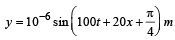 where t is in second and x in meter. The speed of the wave is
where t is in second and x in meter. The speed of the wave is
When two tuning forks (fork 1 and fork 2) are sounded simultaneously, 4 beats per second are heard. Now, some tape is attached on the prong of the fork 2. When the tuning forks are sounded again, 6 beats per second are heard. If the frequency of fork 1 is 200 Hz, then what was the original frequency of fork 2?
An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound, with a velocity one-fifth of the velocity of sound.What is the percentage increase in the apparent frequency ?
A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 HZ and above is approaching a stationary person with speed v ms–1. The velocity of sound in air is 300 ms–1. If the person can hear frequencies upto a maximum of 10,000 HZ, the maximum value of v upto which he can hear whistle is
cm. It is observed to have resonant frequencies of 420 Hz and 315 Hz. There are no other resonant frequencies between these two. Then, the lowest resonant frequency for this string is
A sound absorber attenuates the sound level by 20 dB. The intensity decreases by a factor of
While measuring the speed of sound by perfor ming a resonance column experiment, a student gets the first resonance condition at a column length of 18 cm during winter. Repeating the same experiment during summer, she measures the column length to be x cm for the second resonance. Then
A wave travelling along the x-axis is described by the equation y(x, t) = 0.005 cos (αx –βt). If the wavelength and the time period of the wave are 0.08 m and 2.0s, respectively, then α and β in appropriate units are
Three sound waves of equal amplitudes have frequencies (v –1), v, (v + 1). They superpose to give beats. The number of beats produced per second will be :
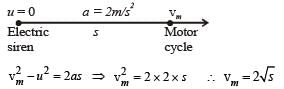
A motor cycle starts from rest and accelerates along a straight path at 2m/s2. At the starting point of the motor cycle there is a stationary electric siren. How far has the motor cycle gone when the driver hears the frequency of the siren at 94% of its value when the motor cycle was at rest? (Speed of sound = 330 ms–1)
The equation of a wave on a string of linear mass density 0.04 kg m–1 is given by
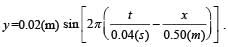
The tension in the string is
The transverse displacement y (x, t) of a wave on a string is given by 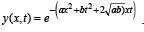 . This represents a:
. This represents a:
A cylindrical tube, open at both ends, has a fundamental frequency, f, in air. The tube is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air-column is now :
A sonometer wire of length 1.5 m is made of steel. The tension in it produces an elastic strain of 1%. What is the fundamental frequency of steel if density and elasticity of steel are 7.7 × 103 kg/m3 and 2.2 × 1011 N/m2 respectively ?
A pipe of length 85 cm is closed from one end. Find the number of possible natural oscillations of air column in the pipe whose frequencies lie below 1250 Hz. The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s.
A train is moving on a straight track with speed 20 ms–1. It is blowing its whistle at the frequency of 1000 Hz. The percentage change in the frequency heard by a person standing near the track as the train passes him is (speed of sound = 320 ms–1) close to :


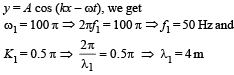
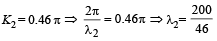
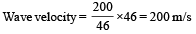
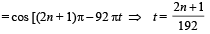
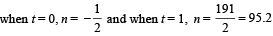

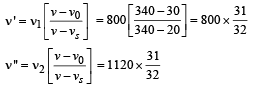
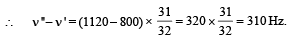
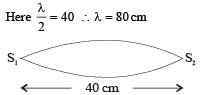
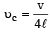 and
and