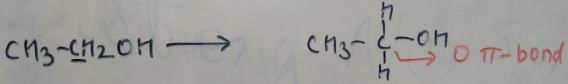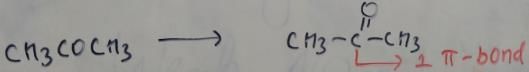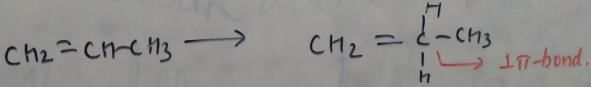Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure
In which of the following species is the underlined "carbon" having sp3-hybridisation?
[AIEEE-2002]
Which of the following is paramagnetic?
[NEET 2013]
A square planar complex is formed by hybridisation of which atomic orbital?
[AIEEE-2002]
The reason for double helical structure of DNA is operation of:
[AIEEE-2003]
Which one of the following pairs of molecules will have permanent dipole moments for both members ?
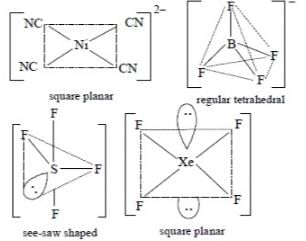
The pair of species having identical shapes for molecules of both species is:
[AIEEE-2003]
The correct order of bond angles (smallest first) in H2S, NH3, BF3 and SiH4 is:
[AIEEE-2004]
The bond order in NO is 2.5 while that in NO+ is 3. Which of the following statements is true for these two species?
[AIEEE-2004]
The states of hybridization of boron and oxygen atoms in boric acid (H3BO3) are respectively:
[AIEEE-2004]
Which one of the following has the regular tetrahedral structure?
[AIEEE-2004]
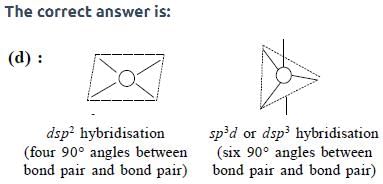
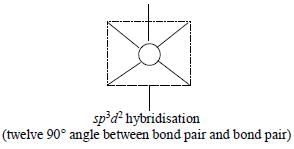
The maximum number of 90° angles between bond pair-bond pair of electrons is observed in:
[AIEEE-2004]
Beryllium and aluminium exhibit many properties which are similar. But, the two elements differ in:
[AIEEE-2004]
Lattice energy of an ionic compound depends upon:
[AIEEE-2005]
The molecular shapes of SF4, CF4 and XeF4 are:
[AIEEE-2005]
Of the following sets which one does not contain isoelectronic species?
[AIEEE-2005]
The number and type of bond between two carbon atom in calcium carbide are:
[AIEEE-2005]
Which of the following molecules/ions does not contain unpaired electron ?
[AIEEE-2006]
Among the following mixtures, dipole-dipole as the major interaction, is present in:
[AIEEE-2006]
A metal, M foms chlorides in its +2 and +4 oxidation states. Which of the following statements about these chlorides is correct?
[AIEEE-2006]
In which of the following molecules/ions are all the bonds not equal?
[AIEEE-2006]
The decreasing value of bond angles from NH3 (106)° to SbH3 (101)° down group-15 of the periodic table is due to:
[AIEEE-2006]
In which of the following ionizion processes, the bond order has increased and the magnetic behaviour has changed
[AIEEE-2007]
Which of the following hydrogen bonds is the strongest
[AIEEE-2007]
The charge/size ratio of a cation determines its polarzing power. Which one of the following sequences represents the increasing order of the polarizing power of the cationic species, K+, Ca+2 Mg+2, Be+2
[AIEEE-2007]
Give reason carbon oxygen bond lengths in formic acid are 1.23 Å & 1.36Å and both the carbon oxygen bonds in sodium formate have the same value i.e. 1.27 Å [JEE' 88]
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
Mark True or False: BeCl2 can be easily hydrolyed [JEE'99]
o-hydroxybenzaldehyde is a liquid at room temperature, while p-hydroxybenzaldehyde is a high melting solid due to [JEE' 99]
N2, O2, F2, Cl2 in increasing order of bond dissociation energy. [JEE' 88]
Arrange in increasing order of dipole moment. [JEE'96]
(I) Toluene, (II) m-dichcorobenzene (III) O-dichlorobenzene (IV) P-dichlorobenzene