Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Tests > Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus.The Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes MCQs are made for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes below.
Solutions of Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes questions in English are available as part of our course for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) & Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes solutions in
Hindi for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
*Multiple options can be correct
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 1
Which of the following statements is/are true?
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 1
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 2
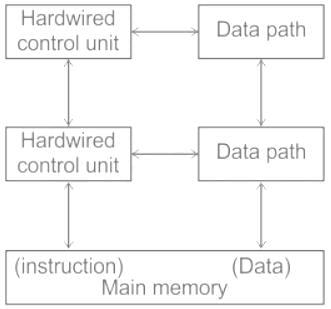
What is the Von Neumann architecture?
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 4
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 5
The following language uses mnemonic OP codes
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 5
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 6
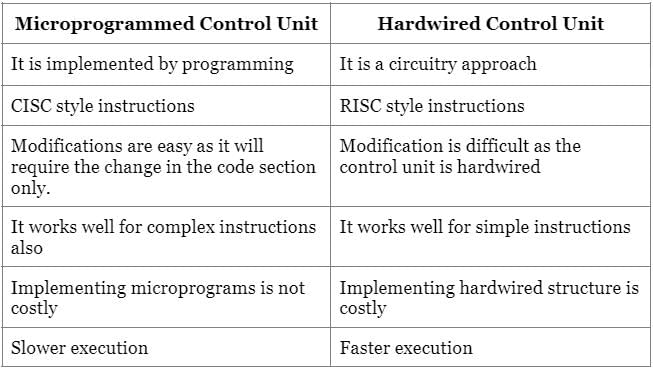
The technology that stores only the essential instructions on a microprocessor chip and thus enhances its speed is referred to as:
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 6
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 7
Which of the following acts as a temporary storage location to hold an intermediate result in mathematical and logical calculations?
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 7
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 8
A register capable of shifting its binary information either to the right or the left is called a _______.
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 8
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 9
The instruction, Add #45,R1 does _______
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 9
Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 10
The addressing mode which makes use of in-direction pointers is ______
Detailed Solution for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes - Question 10
Information about Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Machine Instructions & Addressing Modes, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF